Fig 1. Model structure of compartmental model.
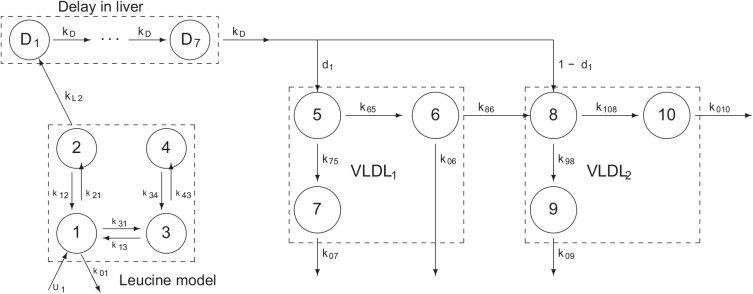
The same structural model was used for all individuals and in both the mixed effects and the STS model. Model constraints, k 2,1 = k 1,2, k 3,4 = 0.1 k 4,3, k 9,8 = k 7,5 and k 0,9 = k 0,7 were used. Compartment 1 represents the free leucine in the plasma, compartments 3 and 4 represents leucine recycling in non-hepatic tissue and compartment 2 is the intrahepatic leucine that feeds the apoB synthesis compartment represented as a delay (D1-D7). Newly synthesized apoB enters the plasma as VLDL1 (large particles, compartment 5) or VLDL2 (small particles, compartment 8). VLDL2 may also be produced through conversion of VLDL1 via compartment 6. Particles may leave the system through compartments 6, 7, 9 or 10.
