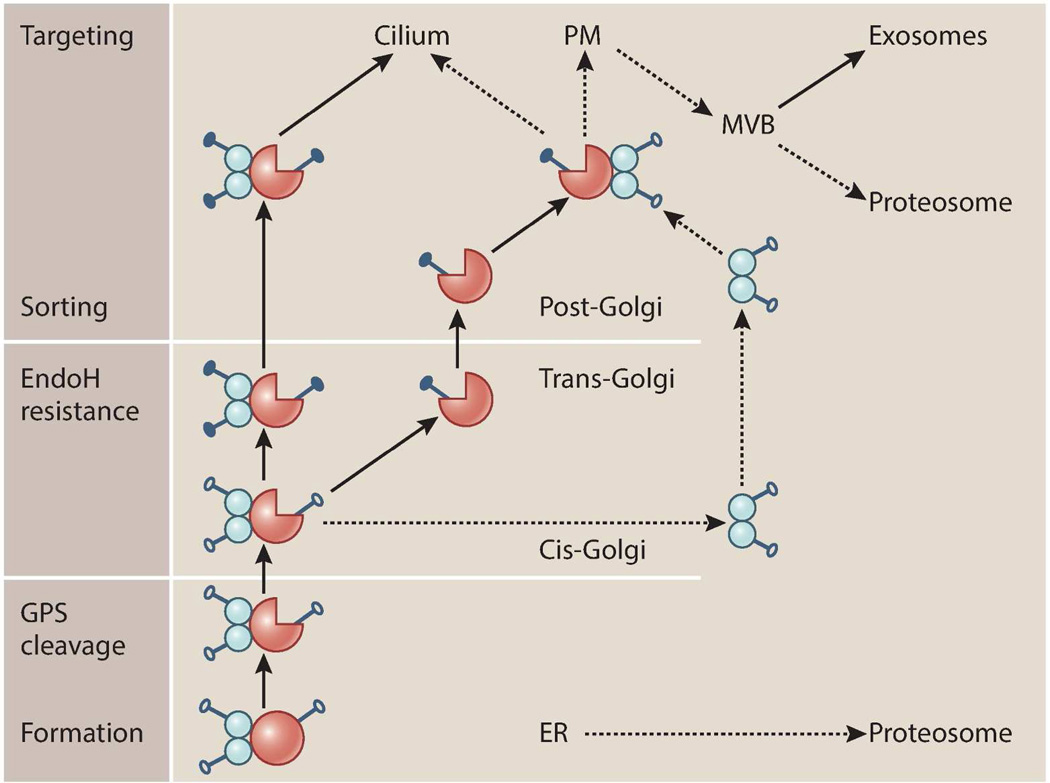
Figure 4. Models of the biosynthesis, maturation and trafficking of the polycystin complex.
PC1 (red) binds to PC2 (blue) shown as a putative dimer in the ER prior to undergoing GPS cleavage. At this stage, both proteins are expressed as EndoH-sensitive glycoforms (empty circles). EndoH-resistance (filled circles) is acquired with passage through the trans-Golgi with a small pool of an EndoH-resistant complex detectable in primary cilia. An alternative model proposes that EndoH-sensitive PC2 exits the cis-Golgi and traffics independently of PC1 which undergoes normal Golgi maturation, acquiring Endo H-resistance. The broken lines indicate other regulatory pathways which could determine the levels of both proteins, complex formation and subcellular localisation.