Figure 1. Bile acid synthesis pathways and mechanism of bile acid feedback regulation.
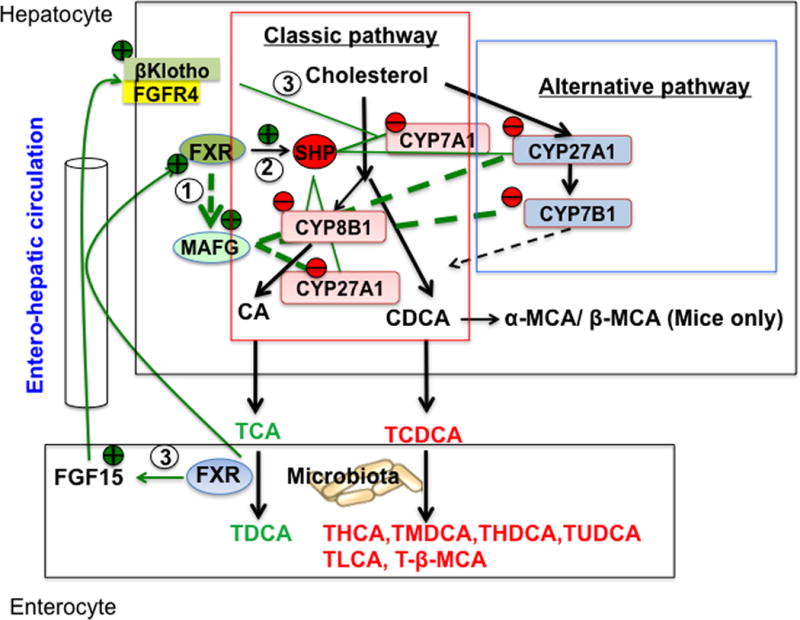
The classic bile acid synthesis pathway is initiated by cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) to synthesize two primary bile acids, cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA). Cholic acid synthesis requires sterol 12α-hydroxylase (Cyp8B1). Mitochondrial sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1) catalyzes steroid-side chain oxidative cleavage. In the alternative pathway, side-chain cleavage by CYP27A1 precedes 7α-hydroxylation by oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7B1) to synthesize oxidized sterols (oxysterols) in most tissues. In mice, CDCA is converted to α- and β-muricholic acids (MCAs). Most bile acids are conjugated to taurine (T) in mice, and secreted into bile, stored in the gallbladder. After each meal, bile acids are secreted into the intestinal tract for absorption and transport of nutrients. In the intestine, bacteria bile salt hydrolase de-conjugated bile acids and then bacteria 7α-dehydroxylase activity removed a 7α-HO group from CA and CACA to form deoxycholic acid (DCA) and lithocholic acid (LCA), respectively, and other secondary bile acids as indicated. FXR/MAFG signaling directly inhibits CYP8B1 and CYP27A1 in the classic pathway and may also inhibit CYP27A1 and CYP7B1 in the alternative pathway (Pathway 1). In the liver, FXR induces SHP to inhibit transactivation of the CYP7A1/CYP8B1 gene (Pathway 2). In the intestine, FXR induces FGF15, which is transported via portal circulation to the liver to activate a membrane FGF receptor 4 (FGFR4)/β-Klotho signaling to inhibit CYP7A1/CYP8B1 gene transcription (Pathway 3). Abbreviations: CYP7A1, cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase; CYP8B1, sterol 12α-hydroxylase; CYP27A1, sterol 27-hydroxylase; CYP7B1, oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase; CA, cholic acid; CDCA, chenodeoxycholic acid; MCA-muricholic acid; DCA, deoxycholic acid; HCA, hyodeoxycholic acid; MDCA, murideoxycholic acid; HDCA, hyodeoxycholic acid; UDCA, ursodeoxycholic acid; LCA, lithocholic acid; FGF15, fibroblast growth factor 15; FGFR4, FGF receptor 4; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; SHP, small heterodimer partner; MAFG, V-Maf Avian Musculoaponeurotic Fibrosarcoma Oncogene Homolog G.T, tauro-conjugated bile acids.
