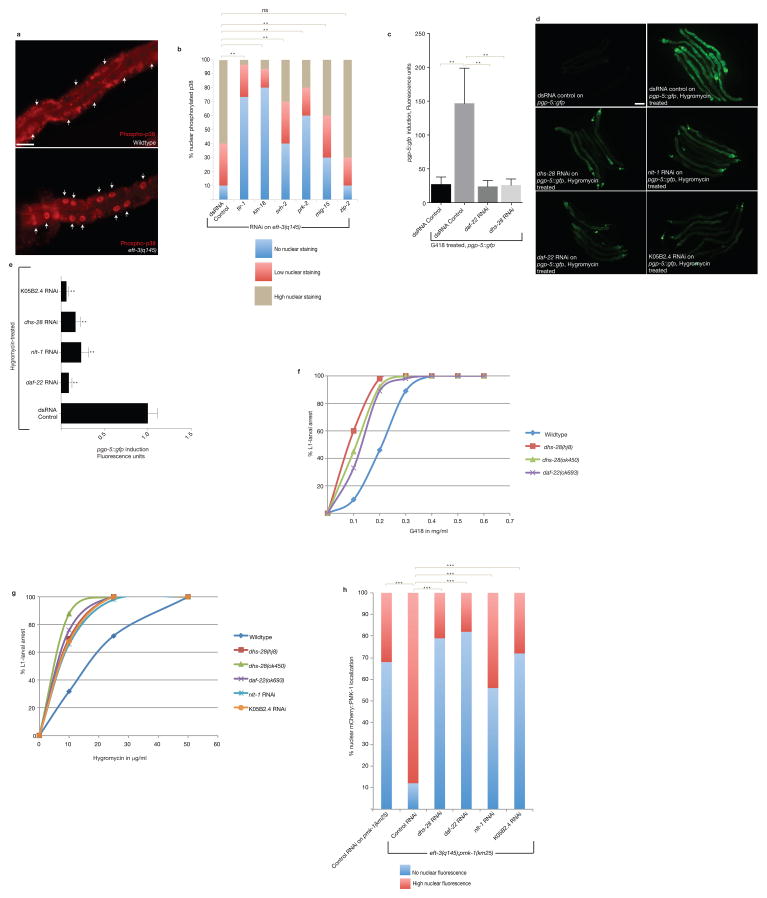
Figure 4. Bile acid-like biosynthetic signaling is required for translation-defective-induced xenobiotic defense response.
A) Germline translation defects in the eft-3(q145);pgp-5::gfp strain causes p38 MAPK phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of active p38 PMK-1 in the intestine. Arrows indicate the nucleus. Scale bar, 20μm.
B) tir-1, kin-18, svh-2, mig-15,and prk-2 are required for germline translation-defect-induced activation of p38 in the intestine. One-way ANOVA; **P<0.01. ns, P>0.05. n=50 (dsRNA control),45 (tir-1 RNAi), 50 (kin-18 RNAi),28 (svh-2 RNAi), 40 (prk-2 RNAi), 50 (mig-15 RNAi) and 32 (zip-2 RNAi) nuclei, respectively. Data represent one out of two independent experiments.
C) Inactivation of lipid and bile acid biosynthetic genes disrupts the induction of pgp-5::gfp in response to G418. Error bars represent SD. One-way ANOVA; **P<0.01. n=413 (dsRNA control non-G418 treated), n=2271(dsRNA control G418 treated), n=239 (daf-22 RNAi),n=514 (dhs-28 RNAi) worms. Data was consolidated from two independent experiments.
D) Lipid and bile acid biosynthetic genes are required for hygromycin-induced pgp-5::gfp. Scale bar, 50μm.
E) Inactivation of genes required for lipid–bile acid biosynthesis disrupts the induction of pgp-5::gfp in response to hygromycin. Error bars represent SD. One-way ANOVA; **P<0.01. n=10 worms for each condition. Data represent one out of two independent experiments.
F) While about 40% of control RNAi treated wildtype animals treated with 0.2 mg/ml G418 grew to adulthood, RNAi of daf-22 and dhs-28 cause >70% of animals treated with 0.2 mg/ml G418 to arrest at L1-larval stage. n=20 worms for each condition. Data represent one out of two independent experiments.
G) Mutations in genes required for lipid–bile acid biosynthesis cause hypersensitivity to G418. n=20 worms for each condition. Data represent one out of two independent experiments.
H) Lipid and bile acid biosynthetic genes are required for germline translation-defective-induced p38 nuclear localization. One-way ANOVA; ***P<0.001. n=50 nuclei (control RNAi on pmk-1 (km25)) and n=42 (control RNAi),32 (dhs-28 RNAi), 18 (daf-22 RNAi), 35 (nlt-1RNAi), and 50 (K05B2.4 RNAi) intestinal nuclei, respectively for eft-3 (q145); pmk-1 (km25). Data represent one out of two independent experiments.