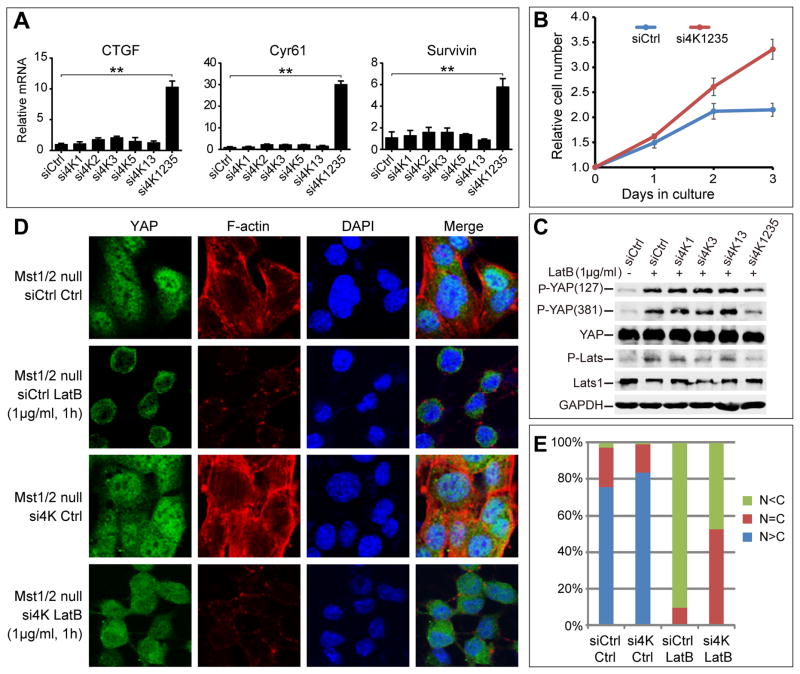
Figure 6. MAP4K1/2/3/5 is required for Hpo/Mst-independent phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion of YAP induced by F-actin disruption.
(A) Concomitant depletion of all four MAP4Ks leads to elevation in the expression levels of three Hpo pathway target genes ctgf, cyr61, and survivin in the Mst1/2 null HCCs. Total RNAs were prepared from HCCs transfected with the indicated siRNAs and the relative mRNA levels of indicated genes were measured by qPCR (mean±SD, n=3). Note the significant increase of gene expression when all four kinases were depleted. ** denotes a p-value<0.01.
(B) Concomitant depletion of all four MAP4Ks promotes the proliferation of Mst1/2 null HCCs.
(C) Depletion of MAP4K1/2/3/5 by RNAi reduces LatB-induced YAP and Lats phosphorylation in the Mst1/2 null HCCs. HCCs cultured on fibronectin-coated surface at low cell density were treated with 1μg/mL LatB for 1 hr and then analyzed by western blotting. Note that LatB induced YAP and Lats phosphorylation (compare lanes 1 and 2). Both inductions were diminished when four kinases were depleted (compare lanes 2 and 6).
(D–E) Depletion of MAP4K1/2/3/5 by RNAi attenuates LatB-induced nuclear exclusion of YAP in the Mst1/2 null HCCs. HCCs transfected with control siRNAs or siRNAs against MAP4K1/2/3/5 were cultured on chamber slides coated with fibronectin at low cell density. Cell were treated with 1μg/mL LatB for 1 hr and then fixed and stained with YAP antibody, phalloidin for F-actin, and DAPI for cell nuclei (C). 100 cells were quantified for YAP localization and the results were shown in (D).
See also Figure S5.