Fig. 1.
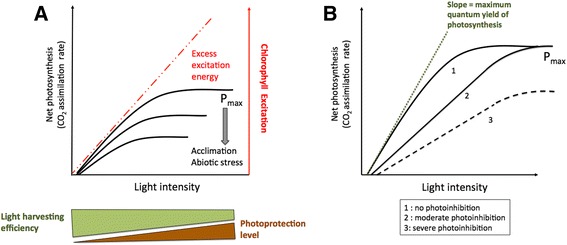
The impact of photoinhibition on leaf photosynthetic efficiency. a: schematic depiction of how excess excitation energy is formed by the saturation of CO2 assimilation and the continued absorption of irradiance. This results in a lowering of light harvesting efficiency under low light as photoprotective processes such as NPQ begin to form and reach a maximum under high light. The proportion of excess excitation energy rises as CO2 assimilation capacity falls. b: schematic depiction of the lowering of quantum yield and maximum photosynthetic capacity according to the severity of photoinhibition (adapted from Murchie and Niyogi 2011)
