FIG 2.
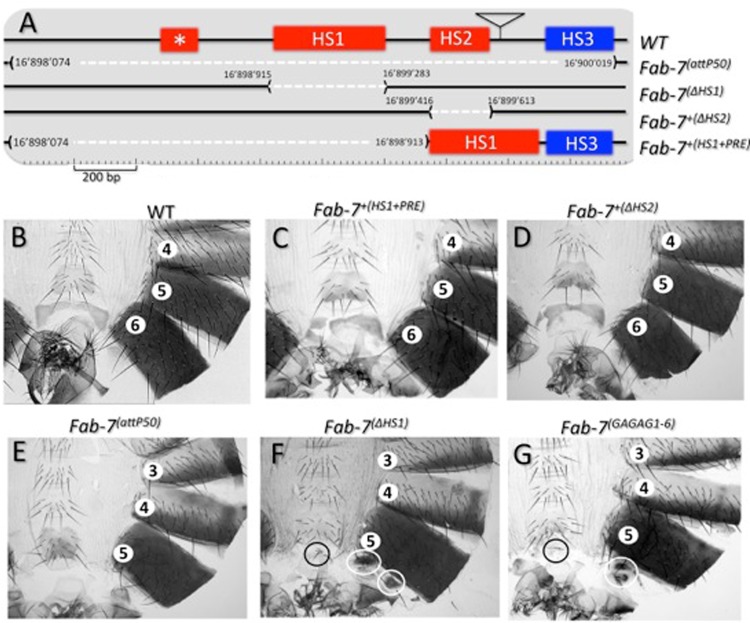
(A) Identifying sequences required for Fab-7 boundary activity in the BX-C. The Fab-7 boundary and abutting PRE (WT) are drawn on top with the four nuclease-hypersensitive regions, *, HS1, HS2, and HS3, as indicated. The location of the bluetail transposon insertion (btl) is indicated by a triangle. Shown in the second line (Fab-7attP50) are the sequences of Fab-7 to the iab-7 PRE that are deleted in the Fab-7attP50 ϕC31 integration platform. Note that this 1,949-bp-long deletion removes all four HS regions as well as flanking DNA sequences (see Materials and Methods). The structures (and coordinates; from release 6 of the BDGP Drosophila genome) of the HS1 and HS2 deletions are indicated in the next two lines [Fab-7ΔHS1 and Fab-7+(ΔHS2)]. The last line in panel A [Fab-7+(HS1+PRE)] shows the structure of the attP50 rescue construct in which only HS1 and HS3 are included. (B to G) Cuticles of the posterior abdominal segments of a wild-type male and of males homozygous for Fab-7+(HS1+PRE) (HS1+ HS3), Fab-7+(ΔHS2), Fab-7attP50, Fab-7ΔHS1, and Fab-7GAGAG1–6, respectively (see Mihaly et al. for a detailed description of cuticular phenotypes [38]). Note that WT males (B) have only six abdominal segments as well as genitalia and analia that are visible at the posterior of each cuticle. The seventh abdominal segments present in embryos and larvae disappear by apoptosis during metamorphosis (93). Because of the GOF transformation of A6 into A7, males homozygous for deletions like Fab-7attP50 (E) that remove both the Fab-7 insulator and the iab-7 PRE have only five abdominal segments (compare panels B and E). While Fab-7+(ΔHS2) males resemble the wild type (compare panels B and D), Fab-7ΔHS1 (F) males exhibit mixed loss- and gain-of-function phenotypes. As expected from a GOF transformation, the A6 segment is significantly reduced in size. On the other hand, the small patches of residual tissues in A6 have a PS10/A5 identity, which is characteristic of a LOF transformation. Fab-7GAGAG1–6 (G) has mutations in GAGA motifs 1 to 6, plus mutations in two GAGAA motifs, as described in the text. Its phenotype is the same as that of Fab-7ΔHS1 (compare panels F and G).