Table 1.
The core structure of indirubin (R5=O) with listed structures and actions of selected synthetic indirubin derivatives. X denotes halogen atoms (Br, I, Cl, and F).
| Indirubin derivatives | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | Main effects/properties | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core structure of indirubins |
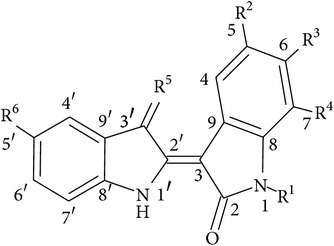
|
|||||||
|
| ||||||||
| Indirubin | -H | -H | -H | -H | =O | -H | Antitumor effect | [4–10] |
|
| ||||||||
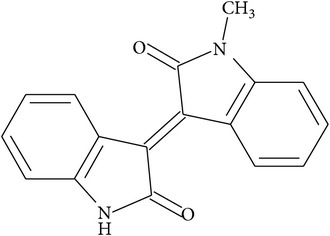
| N-Ethyl-indirubin 5-halogenoindirubins N-Methylisoindigotin (meisoindigo) |
-CH2CH3 | -H | -H | -H | =O | -H | Higher antitumor potencies compared to indirubin | [15–17] |
| -H | -X | -H | -H | =O | -H | |||
| ||||||||
|
| ||||||||
| Indirubin-3′-monoxime | -H | -H | -H | -H | =NOH | -H | Inhibition of CDKs with high potency | [9, 18] |
|
| ||||||||
| 5-Iodoindirubin-3′-monoxime | -H | -I | -H | -H | =NOH | -H | Inhibition of GSK-3β | [19] |
| Indirubin-5-sulfonic acid | -H | -SO3H | -H | -H | =O | -H | ||
| Indirubin-5-sulfonamide | -H | -SO2NH2 | -H | -H | =O | -H | ||
| 5-Halogenoindirubins | -H | -X | -H | -H | =O | -H | ||
|
| ||||||||
| C6 and C5, C6 halogen substit. of indirubin | -H | -H or -X | -X | -H | =O | -H | More potent CDK and GSK-3β inhibitors | [20] |
|
| ||||||||
| 3′-Substituted 7-halogenoindirubins |
-H or -CH3 | -H | -H | -X | =NOH, =NOCH3, =NOCOCH3 and others | -H | Lacking the inhibitory effects towards CDKs and GSK-3β but still inducing cell death | [21] |
|
| ||||||||
| E564 | -H | -H | -H | -H | =NOCH2CH2OCH2CH2OH | -H | Inhibitory effect towards STAT3 signaling, contributing to apoptosis in human cancer cells | [22] |
| E728 | -H | -OCH3 | -H | -H | =NOH | -H | ||
| E804 | -H | -H | -H | -H | =NOCH2CH2CH(OH)CH2OH | -H | ||
|
| ||||||||
| 5-Fluoro-indirubinoxime | -H | -F | -H | -H | =NOH | -H | Antitumor activity in vitro and in several animal models | [23–27] |
| 5-Trimethylacetamino-indirubinoxime | -H | -NH COtBu |
-H | -H | =NOH | -H | ||
| 5-Nitro-indirubinoxime | -H | -NO2 | -H | -H | =NOH | -H | Additional anti-inflammatory properties in HUVECs | [28] |
|
| ||||||||
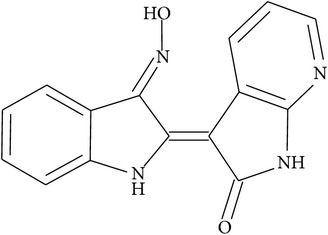
| 7-Azaindirubin-3′-oxime |
|
Potent antiproliferative properties in cancer cell lines and inhibition of a series of kinases | [29] | |||||
|
| ||||||||
| 7-Bromo-5′-carboxyindirubin-3′-oxime | -H | -H | -H | -Br | =NOH | -COOH | Novel inverse binding mode, with improved selectivity for DYRK kinases | [30] |
|
| ||||||||
| 5-Diphenylacetamido-indirubin-3′-oxime | -H | -NHCOC H(C6H5)2 |
-H | -H | =NOH | -H | Novel mitochondria-targeting agent with antileukemic activity | [31] |
|
| ||||||||
| 5′-OH-5-nitro-indirubin oxime (AGM130) | -H | -NO2 | -H | -H | =NOH | -OH | Improved solubility compared to indirubin and effective induction of apoptosis of imatinib-resistant CML cells | [32] |
