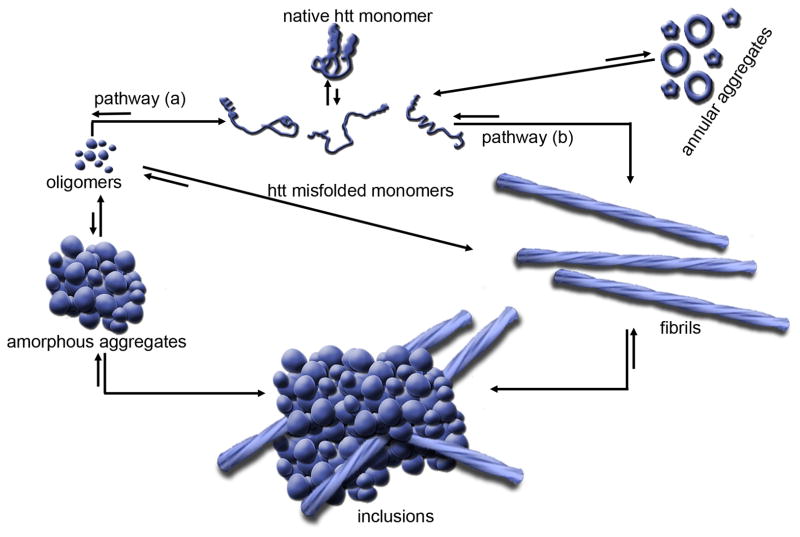
Figure 2. A schematic model for htt aggregation.
A native monomer can sample a variety of distinct, misfolded monomer conformations, with the relative number and stability of these conformers potentially being polyQ length-dependent. Some misfolded monomers likely lead to aggregates, such as annular aggregates, that likely are off-pathway to fibril formation. There appears to be two generic aggregation pathways toward the formation of fibrils structures. (a) One of these pathways proceeds through oligomeric intermediates, some of which may be facilitated by Nt17. The size and stability of oligomeric aggregates can vary widely. A major structural transition must occur within an oligomer to initiate fibril elongation. (b)The other pathway to fibrils is a direct monomer to fibril transition. Oligomerization can also lead to the formation of large amorphous aggregates. All of these higher order aggregates may accumulate together to form the large inclusions that are a hallmark of HD.