Table 1.
Genetic correlations and heritabilities of handling aggression and breathing rate in nestlings (HAn, BRn) and in adults (HAa, BRa). Genetic correlations (upper triangle) and heritabilities (diagonal) are represented as estimate ±s.e. and are derived from the matrix of additive genetic effects estimated by a multivariate animal model. Information on variances and correlations for other components than the additive genetic component are provided in the electronic supplementary material, tables S3 and S4. Fixed effects are reported in the electronic supplementary material, table S5. The significance of a particular genetic correlation was tested by comparing the unconstrained model with models where that genetic correlation (rA) was fixed at 0 using an LRT. The genetic correlations describing the HA–BR behavioural syndrome in the different ontogenetic stages are printed in bold.
| HAn | BRn | HAa | BRa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAn | 0.26 ± 0.04 | –0.49 ± 0.09a | 0.38 ± 0.10b | 0.08 ± 0.11 |
| BRn | 0.28 ± 0.04 | –0.13 ± 0.11 | 0.50 ± 0.11c | |
| HAa | 0.29 ± 0.06 | 0.07 ± 0.16 | ||
| BRa | 0.27 ± 0.06 |
aLRT:  , p < 0.001.
, p < 0.001.
bLRT: 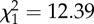 , p < 0.001.
, p < 0.001.
cLRT: 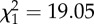 , p < 0.001.
, p < 0.001.
