Figure 1.
Differential Firing Frequencies of PNs and INs during Theta Epochs
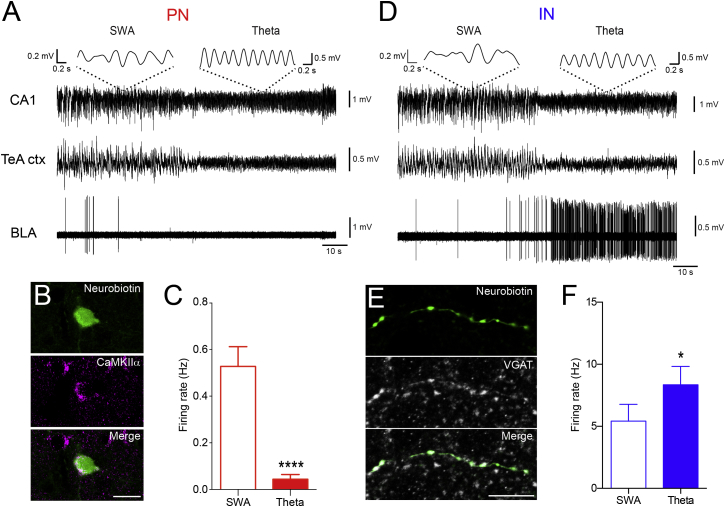
(A) In vivo single unit recording from a representative PN of the BA during SWA and theta oscillations recorded from CA1 HPC and TeA cortex (ctx). This cell became silent at the onset of theta oscillations. Insets show 2 s of CA1 LFP trace band-pass filtered between 2 and 3 Hz (SWA, left) and 3 and 6 Hz (theta oscillations, right).
(B) Juxtacellularly labeled PN displaying immunoreactivity for CaMKIIα.
(C) PNs fired at higher frequencies during cortical and hippocampal SWA (0.52 ± 0.08 Hz) and at significantly lower frequencies during theta oscillations (0.04 ± 0.02 Hz, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 n = 16).
(D) In vivo single unit recording from an IN of the BA during SWA and theta oscillations recorded from CA1 HPC and TeA. The firing frequency increased during theta oscillations. Insets: 2 s of CA1 LFP trace band-pass filtered between 2 and 3 Hz (SWA, left) and 3 and 6 Hz (theta oscillations, right).
(E) Juxtacellularly labeled GABAergic IN displaying axonal immunoreactivity for VGAT.
(F) INs fired at lower frequencies during cortical and hippocampal SWA (5.42 ± 1.35 Hz) and at significantly higher frequencies during theta oscillations (8.35 ± 1.48 Hz, ∗p < 0.05, n = 20). Scale bars: (B), 20 μm; (E), 10 μm. Data are presented as means ± SEM.