Figure 2.
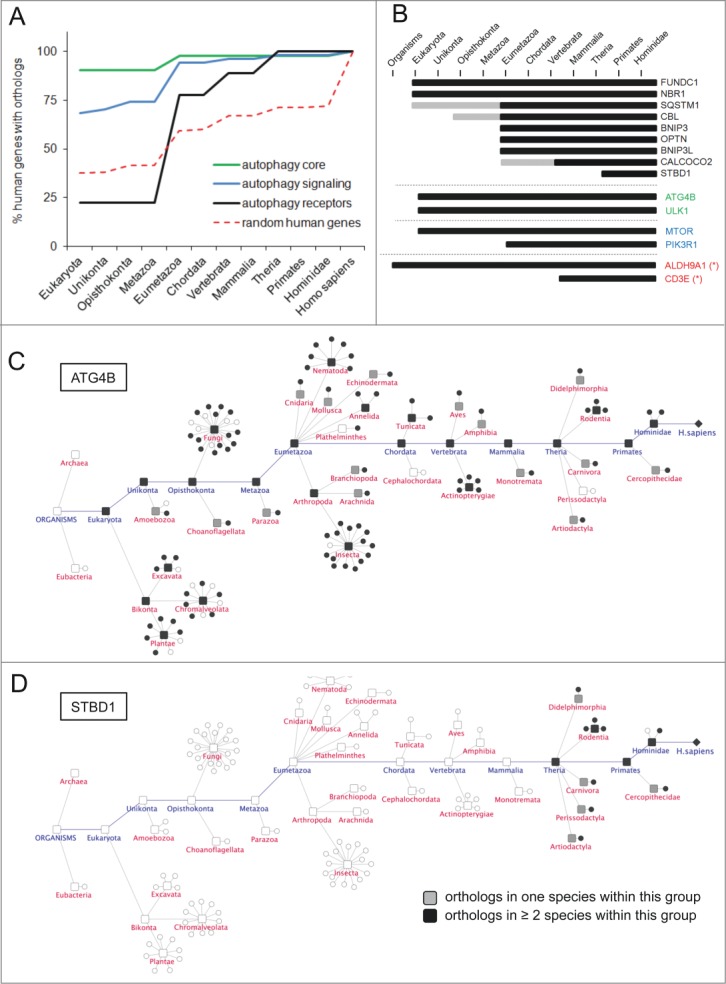
Evolutionary trends of AXAN prime genes. (A) The evolutionary conservation of human genes from functional categories within AXAN was assessed by ortholog identification in 99 eukaryotic model organisms (and Escherichia coli as outgroup) using the InParanoid7 database. Evolutionary trends were displayed as the percentage of conserved human genes in respective phylogenetic groups. Two thousand randomly chosen human genes served as control (red dotted line). (B) Evolutionary conservation of all 9 human autophagy receptors, 2 core genes, 2 signaling genes and 2 non-AXAN control genes (housekeeping enzyme ALDH9A1 and T cell receptor gene CD3E, marked by asterisks). Gray bars, ortholog in one species within this group; black bars, orthologs in at least 2 species within this group. (C and D) Evolutionary tracks of 2 exemplary AXAN genes (core gene ATG4B and receptor STBD1). Circles represent species, and boxes represent higher order taxonomic groups containing these species. Presence of an ortholog in a given species is visualized by black symbols. For higher groups, coloring displays presence of orthologs in one (gray) or at least 2 (black) species within this group. As examples, the highly conserved autophagy core gene, ATG4B, and the autophagy receptor gene, STBD1, (the most recent autophagy receptor) are displayed.
