Figure 4.
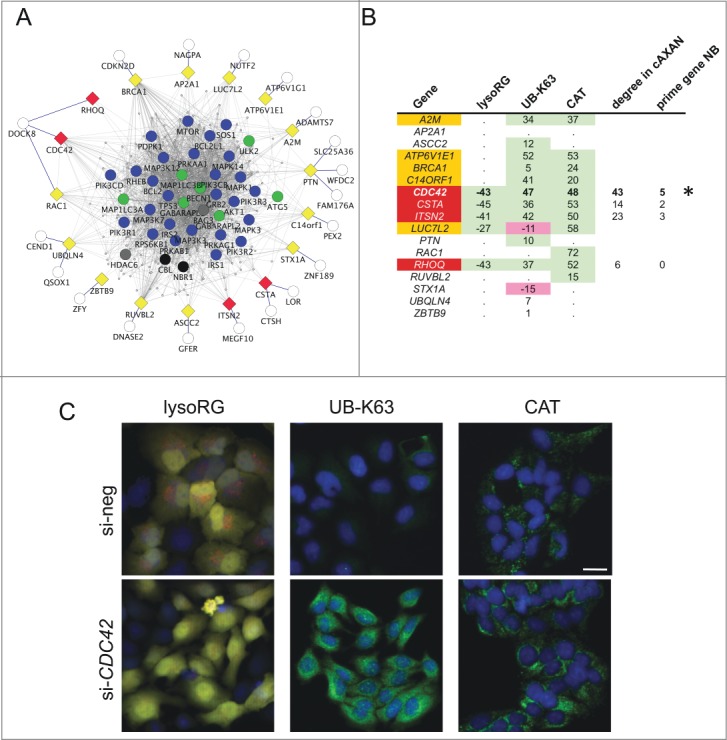
Functional assessment of network predictions. (A) External linker nodes (diamonds) were introduced to connect hitherto solitary nodes (white circles) to AXAN main network (color coding of prime genes as described above). Only those linker nodes chosen for functional siRNA-screening and their first-degree neighbors are shown. Yellow, candidate linker genes that did not pass all test criteria; red, hit genes from functional screen. (B) Summary of the results from a tripartite image-based siRNA screen aimed to assess the role of linker nodes for autophagy pathways. Three independent assays were used: delivery of the cytosolic RFP-EGFP fusion protein to the lysosome (lysoRG) as a measure of autophagy, quantification of endogenous Lys63/K63-linked ubiquitin (UB-K63) levels and quantification of peroxisomal mass (using CAT/catalase as an endogenous marker) under pexophagy conditions (CT, as a measure of pexophagy). Effect strength is displayed using si-negCTRL normalized values. Purple, gene knockdown decreases autophagy effect; green, knockdown increases effect. Of 17 candidate genes tested, 5 passed 2 of the 3 tests with effects in the same direction (orange), and 4 passed all 3 tests in the same direction (red). CDC42 (marked by asterisk) was chosen for further analyses, based on effect strength, its degree in cAXAN and the number of prime genes among its direct neighbors (NB). (C) Examples of how knockdown of Rho GTPase, CDC42, affects the 3 image-based readouts (Scale bar: 10 μm).
