Figure 1.
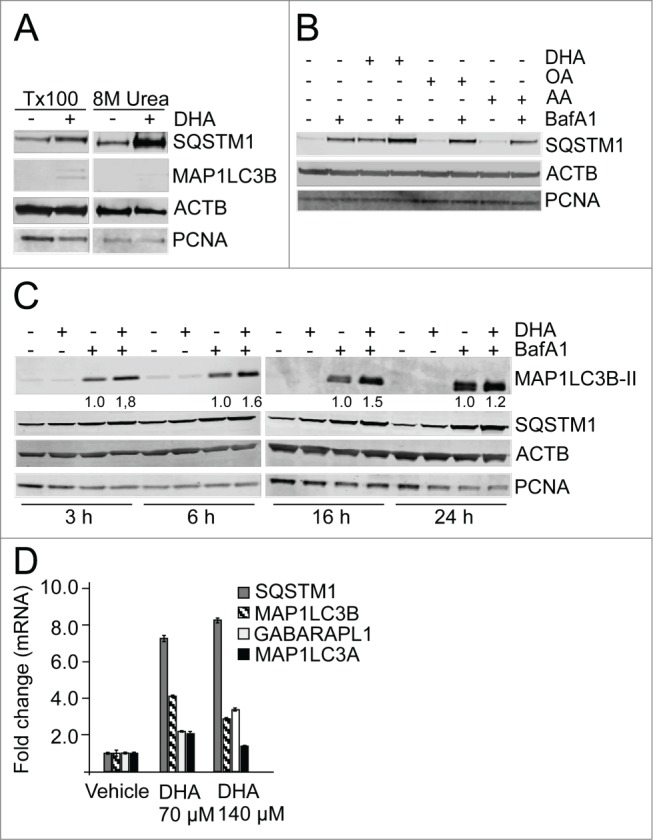
The n-3 PUFA DHA increases protein level of SQSTM1 and induces autophagy in ARPE-19 cells. (A) Cells were treated with DHA (70 µM) for 24 h and lysed in Triton X-100 (Tx100) buffer. Equal amounts of protein (20 µg) from T × 100 fraction were centrifugated at 10,000 x g and the pellet was dissolved in the same volume of 8 M urea buffer before loading on the gel. The membrane was immunoblotted for SQSTM1 and MAP1LC3B. β-actin (ACTB) and PCNA are used as loading controls. (B) The cells were treated with DHA, OA or AA (70 µM) with or without BafA1 (100 nM) for 16 h. Total cell extracts were immunoblotted for SQSTM1. ACTB and PCNA are used as loading controls. (C) Protein levels of SQSTM1 and MAP1LC3B determined by immunoblotting of cells treated with DHA (70 µM), BafA1 (100 nM) or a combination of DHA and BafA1 for the indicated time points. The numbers below the MAP1LC3B-II bands represent fold change relative to BafA1 for each time point normalized to PCNA intensity. ACTB and PCNA are used as loading controls. (D) The mRNA levels of SQSTM1, MAP1LC3B, MAP1LC3A, and GABARAPL1 relative to ACTB after DHA (70 and 140 µM) supplementation for 16 h determined by quantitative real-time PCR. qRT-PCR data displayed are representative for 2 independent experiments. Mean fold change from triplicate wells ± SD is displayed. Data shown are representative of 3 or more independent experiments, unless otherwise stated.
