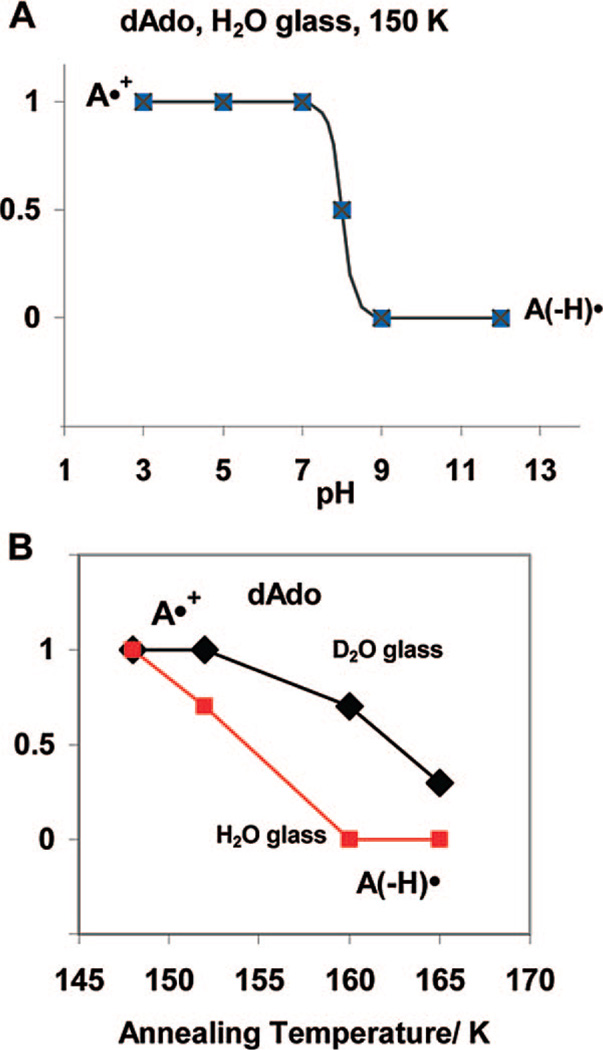
Figure 4.
(A) The schematic diagram shows that A•+ is found for pH’s up to 7 and A(−H)• is found at pH’s of 9 and above at 150 K in 7.5 M LiCl H2O or D2O glasses. At pH 8, equal amounts of A•+ and A(−H)• are found; the pKa of A•+ is therefore ca. 8 at 150 K in these systems. In D2O glassy samples, the corresponding pKa of A•+ is ca. 8.5. (B) The prototropic equilibrium of A•+ is found at 150 K. However, annealing to a slightly higher temperature of ca. 160 K and above allows for molecular migration, and deprotonation is found at all pH’s investigated, i.e., 3 to 12, in H2O glasses. In D2O glasses, which soften at slightly higher temperatures, deprotonation of A•+ is nearly complete at 165 K.