Figure 3.
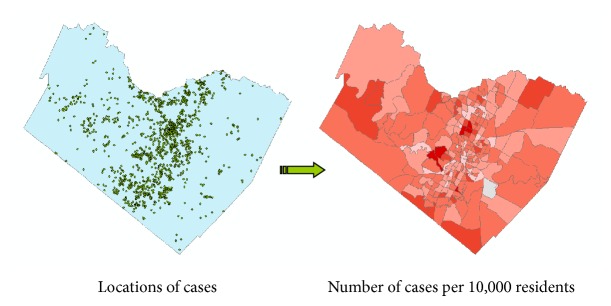
Spatial aggregation of individual cases using census enumeration units. Individual geocoded locations (left) are aggregated using census tracts (right). The count of the number of cases per census tract is used to determine relevant population-weighted indices, such as the number of cases per 10,000 residents. Determining incidence or disease rates, as opposed to raw counts, is one of the primary reasons for aggregation. As a secondary benefit, spatial aggregation greatly reduced the reidentification risk.
