Fig.3.
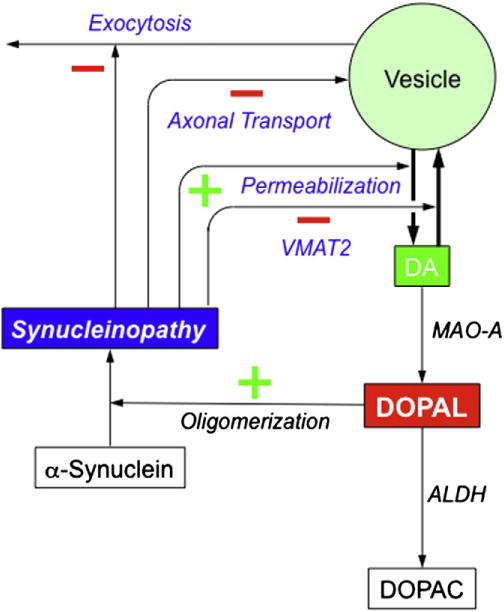
Potential mechanisms of synucleinopathy-induced augmentation of DOPAL production. Synucleinopathy might increase DOPAL formation by inhibiting VMAT2 expression or functions, permeabilizing vesicles, interfering with axonal transport (thereby decreasing vesicle numbers in striatal dopaminergic terminals), and inhibiting exocytosis.
