Figure 1.
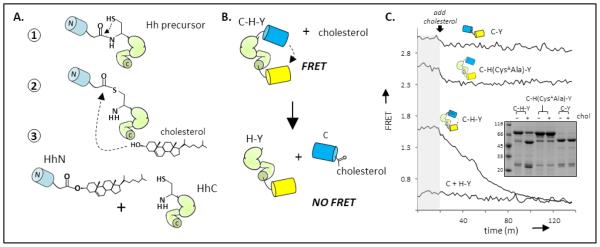
Mechanism and monitoring of Hh cholesterolysis. (A) Reaction pathway. Cholesterolysis of Hh precursor proteins involves an N-S acyl shift at a conserved glycine-cysteine dipeptide (step 1); transesterification to cholesterol (step 2); and dissociation of cholesteroylated Hh ligand (HhN) from the Hh autoprocessing segment, (HhC) (step 3). (B) FRET reporter of cholesterolysis. Construct, abbreviated C-H-Y, contains HhC as an internal fusion to Cyan fluorescent protein and Yellow fluorescent protein. (C) Cholesterolysis assay. FRET from catalytically active C-H-Y, and inactive control constructs,C-Y and C-(CysAAla)H-Y, are monitored before and after cholesterol addition. The kinetic trace of C-H-Y shows FRET loss following cholesterol addition, approaching FRET of a 1:1 mixture of CFP and YFP. Inset Characterization of cholesterolysis reactions by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. Molecular weights: C-H-Y, 80 kDa; CFP, 27 kDa; H-Y, 52 kDa; C-Y, 48 kDa.
