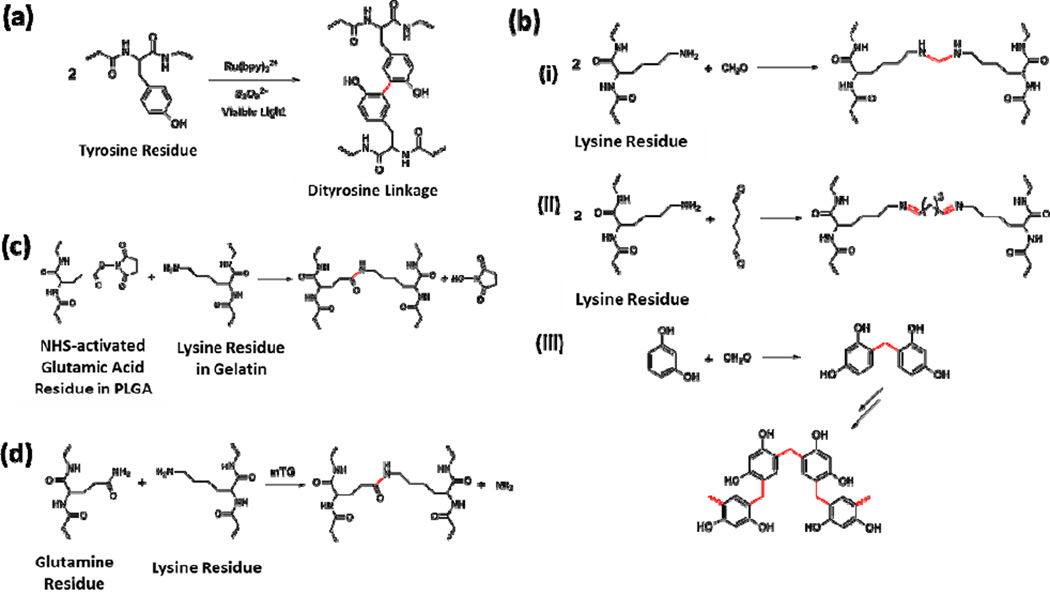
Figure 2.
Typical reactions used for crosslinking in polypeptide/protein-based sealants. (A) Ru-catalyzed visible light promoted reaction to chemically crosslink tyrosine-containing proteins and polypeptides via the formation of dityrosine linkages [30]. (B) Crosslinking mechanism of GRF or GRFG sealants, including (i) the reaction between lysine residues and formaldehyde, (ii) Schiff base formation between lysine residues and glutaraldehyde, and (iii) formation of the network structure from formaldehyde and resorcinol [39–41]. (C) Reaction between NHS-activated poly(L-glutamic acid) and gelatin [42]. (D) Reaction between the glutamine residue and lysine residue catalyzed by mTG [46].