Fig 4. Mutation of acetylated lysine residues results in mislocalization of NDPK-D.
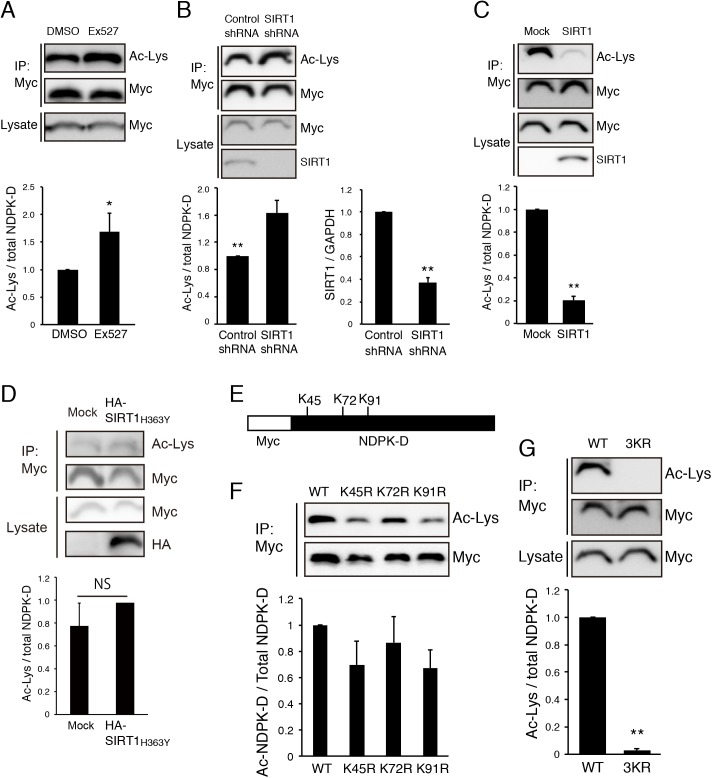
(A) Inhibition of SIRT1 increased acetylation level of NDPK-D. N1E-115 cells were transfected with Myc-NDPK-D, treated with SIRT1 inhibitor Ex527, and cultured for 48 h. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody and the immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with anti-acetylated lysine (Ac-Lys) antibody. The Ac-Lys signal intensity was quantified by densitometry and normalized to the signal intensity of precipitated Myc-NDPK-D. *P < 0.05. n = 3. (B) Knockdown of SIRT1 increased acetylation level of NDPK-D. N1E-115 cells were transfected with Myc-NDPK-D and control or SIRT1 shRNA. The acetylation level of NDPK-D was tested as described in (A). **P < 0.01. n = 6. SIRT1 shRNA efficiently reduced Sirt1 mRNA expression in N1E-115 cells (right panel). **P < 0.01. n = 3. (C, D) SIRT1, but not catalytic-dead point mutant (H363Y) deacetylates NDPK-D in N1E-115 cells. Cells were transfected with Myc-NDPK-D and HA-SIRT1 (C) or HA-SIRT1 H363Y (D), and the acetylation levels of Myc-NDPK-D were determined by anti-Ac-Lys antibody. NS: not significant. **P < 0.01. n = 5 (C), n = 3 (D). (E) Schematic representation of lysine residues in NDPK-D. Lys-45, Lys-72, and Lys-91 were candidate acetylation sites. (F) N1E-115 cells were transfected with Myc-tagged wild-type NDPK-D, the K45R, K72R, or K91R mutants. Acetylation levels were determined as described in (A). Replacement of lysine residues with arginine decreased acetylation levels. n = 3. (G) N1E-115 cells were transfected with Myc-tagged wild-type (WT) NDPK-D or the K45/72/91R (3KR) mutant. Acetylation levels were determined as described in (A). **P < 0.01. n = 6. Statistical analyses were performed using Welch’s t-test (A-D, G).