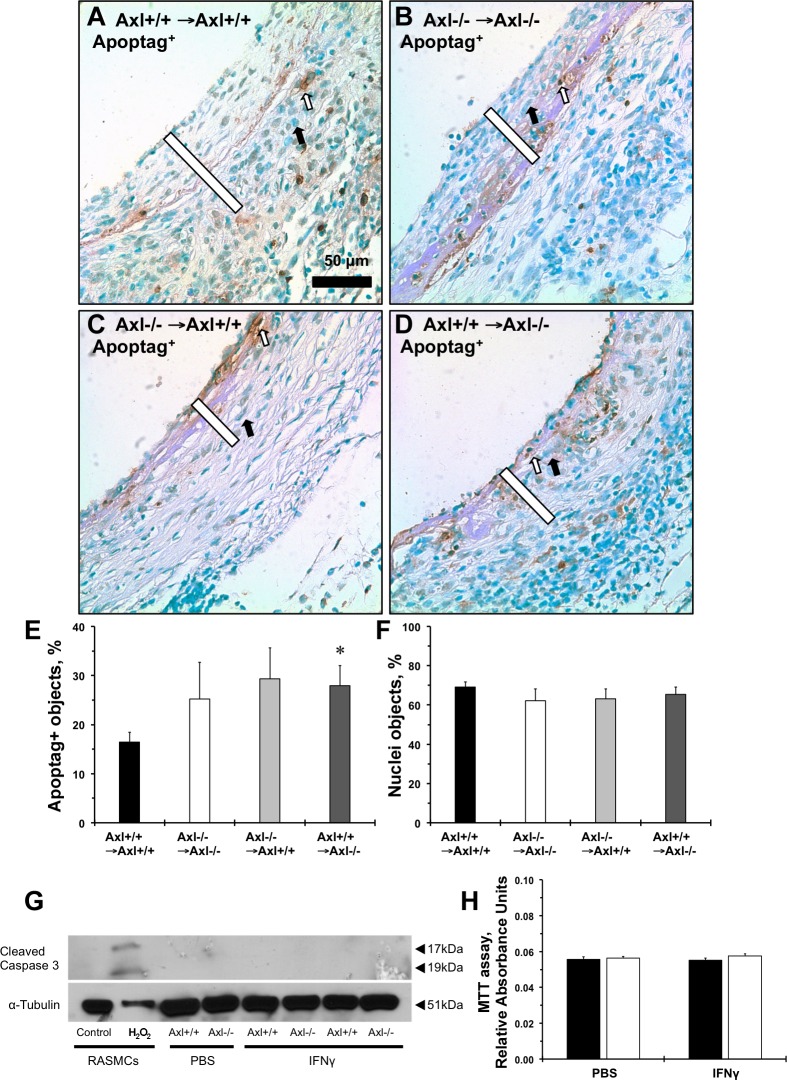
Fig. 4.
Role of Axl on vein graft apoptosis and after immune stimulation of cultured SMCs. Representative Apoptag staining of grafts from Axl+/+ → Axl+/+ mice (A), Axl−/− → Axl−/− mice (B) Axl−/− → Axl+/+ mice (C), and Axl+/+ → Axl−/− (D) is shown. Apoptotic cells are stained in dark brown (open arrows). Counterstained cells are green (solid arrows). Open bars show the intima + media graft areas. Scale bar = 50 μm. E: quantification of Apoptag-positive cells in vein grafts (in %). F: relative number of counterstained nuclei in vein grafts (in %). Values are means ± SE; n = 3–4 mice/group. *P < 0.05 compared with the Axl+/+ → Axl+/+ group. G: representative immunoblots of cleaved caspase-3 after IFN-γ stimulation for 24 h in MASMCs. Rat aortic SMCs (RASMCs) were treated with H2O2 and used as a positive control. α-Tubulin was used as loading control. H: MTT assay of SMCs treated with PBS or IFN-γ for 24 h. Solid bars are Axl+/+ MASMCs; open bars are Axl−/− MASMCs. Values are means ± SE; n = 3 mice/group.