Figure 6.
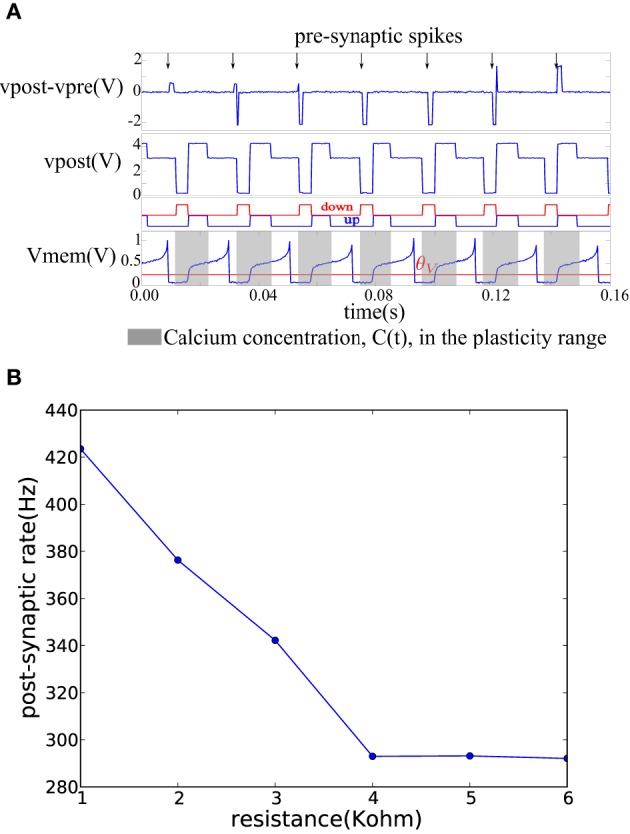
(A) Membrane potential and the ′up′ and ′dn′ signals of a post-synaptic tile receiving spikes at a constant rate from a pre-synaptic tile. The plasticity circuit controls the post-synaptic terminal potential so as to generate an appropriate programming/read pulse across the vpost − vpre terminals on each pre-synaptic spike. (B) Decrease of post-synaptic neuron firing frequency as the conductance of the afferent synaptic element decreases while the pre-synaptic neuron firing rate is kept constant.
