Fig. 2.
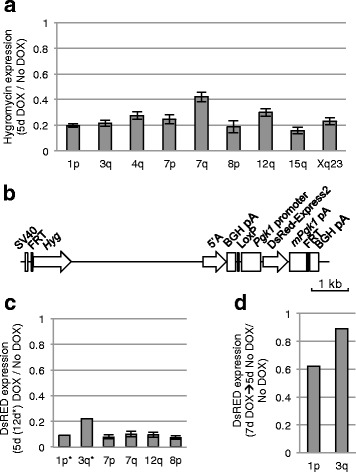
Silencing of flanking reporter genes upon XIST expression from various integration sites. a Relative level of Hyg expression after 5 days of XIST expression induced by DOX treatment compared with no DOX levels, measured by q-RT-PCR, for each of nine different integration sites as listed. Error bars show the standard deviation of biological triplicates. A one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test gives the following differences: 1p and 7q**, 3q and 7q**, 7p and 7q*, 7q and 8p**, 7q and 15q***, 7q and Xq** (*P ≤0.05; **P ≤0.01; ***P ≤0.001). b Map of transgene containing an inducible construct of the 5’A repeats of XIST as well as a DsRed-Express2 reporter gene expressed from a constitutive Pgk1 promoter. c Silencing of DsRed-Express2 relative to no DOX cells, measured by flow cytometry, after 5 or 12 days of DOX induction of 5’A region of XIST (from construct shown in part b) that had been integrated into six different integration sites as listed. The error bars represent ±1 s.d. of the silencing levels of individual single-cell clones (N = 8–11). d DsRed-Express2 expression, measured by flow cytometry, following induction (7 days DOX) and subsequent repression (5 days no DOX) of repeat A of XIST at two integration sites (1p and 3q)
