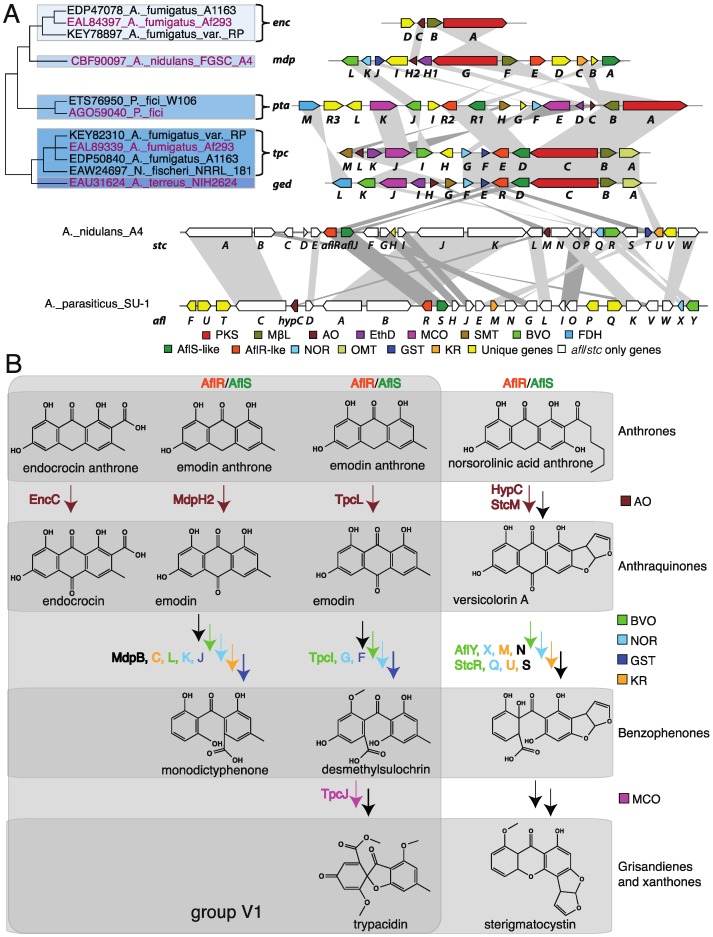
Figure 4.
(A) A phylogenetic tree created from the group V maximum likelihood tree (Figure S2) showing just the relationships between the characterized group V1 PKSs. The gene cluster diagrams next to brackets depict the cluster corresponding to the PKS with its accession number highlighted in red, but all of the bracketed PKSs belong to clusters which are identical in terms of the presence and synteny of their group V-cluster homologs. Genes are represented as arrows with a color corresponding to their ortholog group and these are connected by shaded regions. Genes colored in yellow are unique among clusters shown here. Genes with no color in the afl and stc clusters do not have a homolog in the group V1 clusters shown; (B) A comparison of the analogous reactions catalyzed by the enzymes encoded by homologs of afl cluster genes in the endocrocin, monodictyphenone, trypacidin, and aflatoxin pathways. The reactions of the trypacidin pathway are representative of the geodin and pestheic acid biosynthetic pathways. Pathways of group V1 clusters are enclosed in a grey box. The enzymes catalyzing each reaction are shown to the left of the arrows and the color of the text and arrows matches Figure 4A. Arrows in black represent reactions not shown or reactions for which the enzymes, also labeled in black, are not homologous, except for AflN and StcS, which are homologous. PKS = Polyketide synthase, MβL = Metallo-β-lactamase-type thioesterase, AO = Anthrone oxidase, EthD = EthD domain-containing protein, a putative decarboxylase [51,53], MCO = multicopper oxidase, SMT = S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase, BVO = Baeyer-Villiger oxidase, FDH = Flavin-dependent halogenase, AflS = Transcriptional co-regulator of the aflatoxin biosynthetic gene cluster [76], AflR = Transcriptional regulator of the aflatoxin biosynthetic gene cluster, NOR = NADH-dependent oxidoreductase, OMT = O-methyltransferase, GST = Glutathione S-transferase, KR = Ver-1-like ketoreductase [77,78].