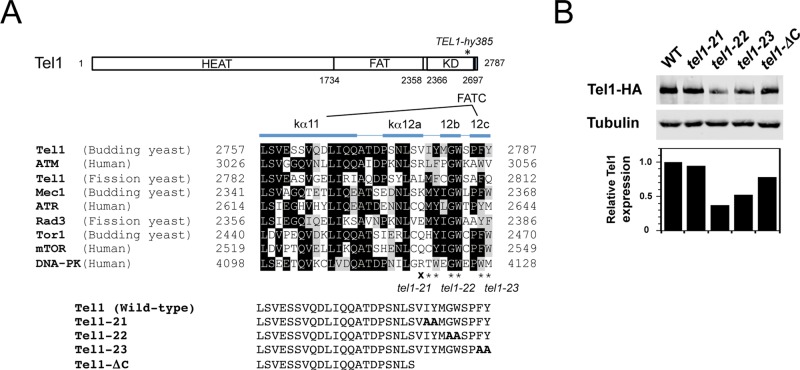
FIGURE 1:
Substitution and truncation mutations of Tel1 at the conserved extreme C-terminal region. (A) Schematic of tel1 mutations at the FATC domain. Tel1 possesses a kinase domain (KD) within the C-terminal portion. The aligned sequences are derived from the FATC domains of ATM-family proteins (Tel1, human ATM, and fission yeast Tel1), ATR family proteins (Mec1, human ATR, and fission yeast Rad3), TOR proteins (budding yeast Tor1 and human mTOR), and human DNA-PK. Identical amino acid residues are boxed in black. Related amino acid residues are highlighted in gray. The α-helix structures kα11 and kα12 (12a, 12b, 12c) are adopted from Yang et al. (2013). The tel1-21, tel1-22, and tel1-23 mutations change the amino acid residues into alanine at positions 2779–2780, 2782–2783, and 2786–2787 (indicated by asterisks), respectively. The tel1-ΔC mutation introduces the termination codon for the amino acid residue at 2778 (indicated by X), truncating the amino acid residues from 2778 through 2787. The HEAT repeats and the FAT domains are shown as well. The residue numbers of the FAT and KD domains for Tel1 are indicated along with the overall Tel1 structure. The mutation site of TEL1-hy385 is shown on the overall structure (Baldo et al., 2008). (B) Expression level of Tel1 in tel1-21, tel1-22, tel1-23, and tel1-ΔC mutants. Top, cells expressing Tel1-HA (KSC1709), Tel1-21-HA (KSC3087), Tel1-22-HA (KSC3088), Tel1-23-HA (KSC3089), or Tel1-ΔC-HA (KSC3549) were subjected to immunoblotting analysis with anti-HA or anti-tubulin antibodies. Bottom, protein levels of Tel1 were normalized to tubulin and expressed relative to the wild type.