Figure 1.
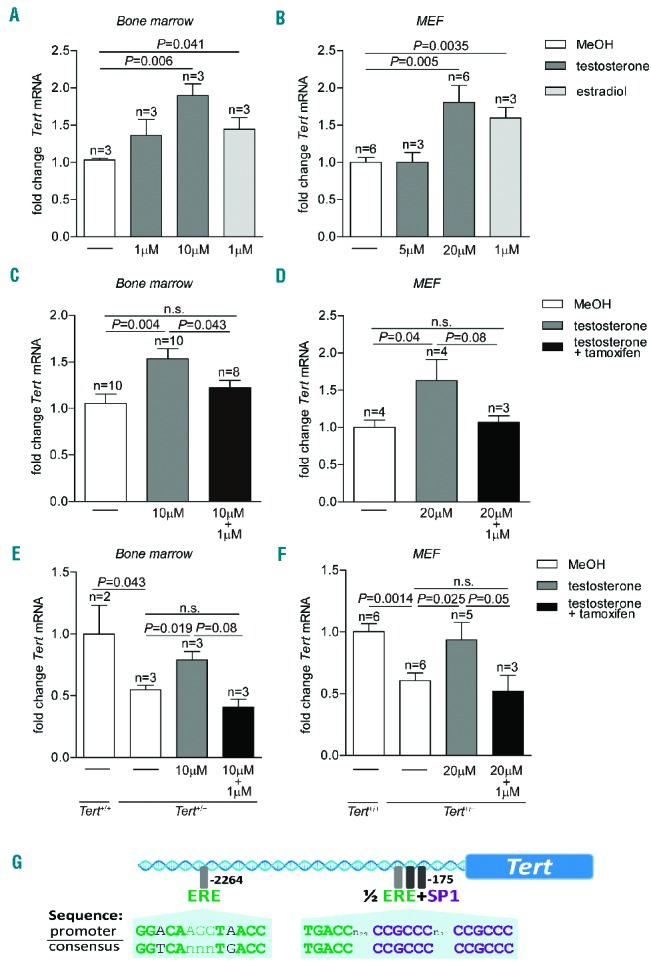
Tert activation by testosterone in vitro. (A) Fold change of Tert mRNA in murine bone marrow cells treated with testosterone or estradiol at indicated concentrations. (B) Fold change of Tert mRNA in MEF treated with testosterone or estradiol at indicated concentrations. (C) Fold change of Tert mRNA in murine bone marrow cells treated with testosterone and testosterone in combination with 1 μM 4-hydroxytamoxifen. (D) Fold change of Tert mRNA in MEF treated with testosterone and testosterone in combination with 1 μM 4-hydroxytamoxifen. (E) Fold change of Tert mRNA in Tert+/+ and Tert+/− bone marrow cells. Tert+/− cells were incubated with testosterone and testosterone in combination with 1 μM 4-hydroxytamoxifen. (F) Fold change of Tert mRNA in Tert+/+ and Tert+/− MEF. Tert+/− cells were incubated with testosterone and testosterone in combination with 1 μM 4-hydroxytamoxifen. All graphs show mean values, error bars indicate SEM, n = number of samples from different mice or MEF clones. A one-sided Student t-test was used for the statistical analysis. P-values are indicated. n.s. = not significant. (G) Illustration of putative binding sites for the estrogen receptor (ERE) and the Sp1 transcription factor in the promoter region of the mouse Tert gene.
