FIGURE 8.
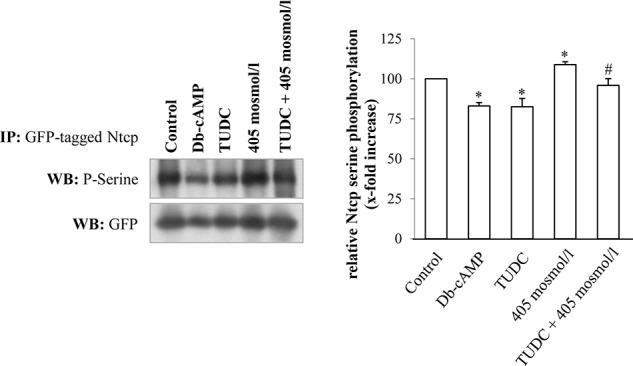
TUDC and cAMP induce serine dephosphorylation of Ntcp in HepG2-Ntcp cells. Ntcp-transfected HepG2 cells were stimulated with either TUDC (100 μmol/liter), Bt2cAMP (10 μmol/liter) under normo-osmotic (305 mosmol/liter) conditions, or with hyperosmotic medium (405 mosmol/liter) without and with TUDC. GFP-tagged Ntcp was analyzed with regard to serine phosphorylation. Treatment with TUDC as well as treatment with Bt2cAMP resulted in decreased serine phosphorylation, although hyperosmolarity triggered an increase in serine phosphorylation of the Ntcp. Ntcp serine phosphorylation was analyzed by Western blot (WB) and subsequent densitometric analysis. GFP served as a loading control. Ntcp serine phosphorylation under control condition was set to 100%. Data represent means ± S.E. of at least five independent experiments. IP, immunoprecipitation. *, p < 0.05 statistically significant compared with the unstimulated control. #, p < 0.05 statistical significance between hyperosmolarity and hyperosmolarity plus TUDC.
