FIGURE 7.
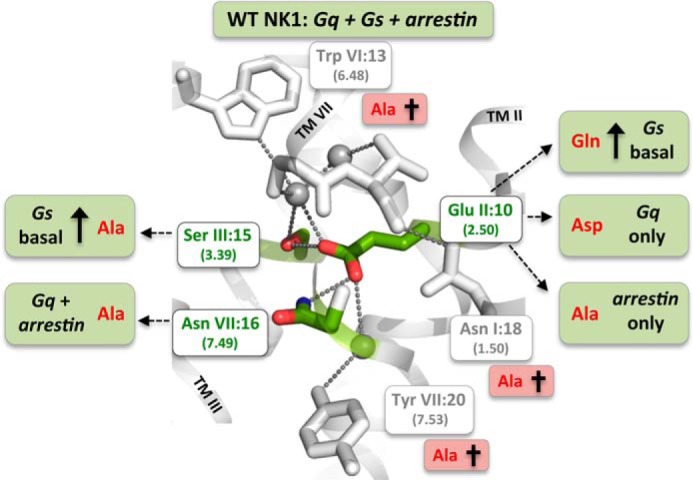
Residues of the water hydrogen bond network of the NK1 receptor identified to be either essential for overall signal transduction or for the fine-tuning and bias of signaling through the three different signaling pathways: Gs, Gq, and β-arrestin. Three residues were by Ala substitutions identified to be essential for all three signal transduction pathways as follows: the water-gating TrpVI:13 (6.48) of the CWXP motif and the TyrVII:20 (7.53) of the NPXXY motif as well as the ultra-highly conserved TM-VII kink-stabilizing AsnI:18 (1.50). Mutations of GluII:10 (2.50) and the two residues SerIII:15 (3.39) and AsnVII:16 (7.49), to which GluII:10 according to the molecular models makes direct hydrogen bond interactions, result in receptor mutants with biased signaling as follows: β-arrestin only (GluII:10 to Ala), Gq only (GluII:10 to Asp), high constitutive Gs signaling (GluII:10 to Gln), and Gq plus β-arrestin but not Gs (AsnVII:16 to Ala). Ala substitution of SerIII:15 selectively increases Gs signaling from zero to ∼40% of Emax.
