FIGURE 1.
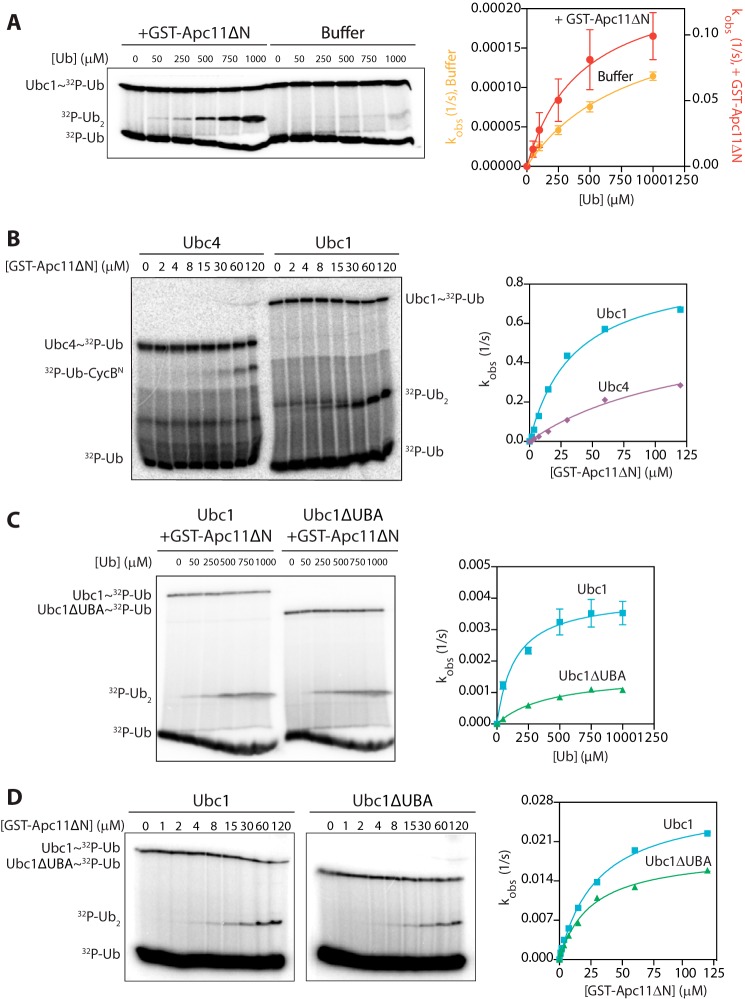
The UBA domain does not contribute to acceptor ubiquitin binding or RING enhancement of E2 catalysis. A, Ubc1 (wild type; 0.5 μm) was charged with 32P-radiolabeled K48R ubiquitin and incubated with either GST-Apc11ΔN (80 μm) or buffer. Wild-type ubiquitin was added at the indicated concentrations, and reactions were carried out at 4 °C for 5 s (+GST-Apc11ΔN) or 10 min (buffer alone). Reaction products were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography with a phosphorimaging system. The right panel displays the quantification of diubiquitin synthesis assays, showing the dependence of catalytic rate (kobs) on ubiquitin concentration. Autoradiographs were quantified using ImageQuant, and data were fit to the Michaelis-Menten equation in Prism software. The average of three experiments is shown. Error bars represent S.E. B, Ubc1 (wild type) and Ubc4 (each at 0.5 μm) were charged with 32P-radiolabeled K48R ubiquitin and incubated with buffer or increasing concentrations of GST-Apc11ΔN. Unlabeled CycBN (200 μm; Ubc4 reactions) or ubiquitin (100 μm; Ubc1 reactions) was added, and reactions were carried out at 4 °C for 5 s. Reactions were analyzed as in A. Results are representative of three independent experiments. C, Ubc1 (wild type or ΔUBA at 0.5 μm) reactions were carried out as in A except that a subsaturating concentration of GST-Apc11ΔN (6.5 μm) was used. Reactions were carried out at room temperature for 3 (wild-type Ubc1) or 5 min (Ubc1ΔUBA). The average of three experiments is shown. Error bars represent S.E. D, Ubc1 and Ubc1ΔUBA were charged as in A and incubated with buffer or increasing concentrations of GST-Apc11ΔN. Unlabeled wild-type ubiquitin (100 μm) was added, and reactions were carried out, visualized, and quantified as in A. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Ub, ubiquitin.