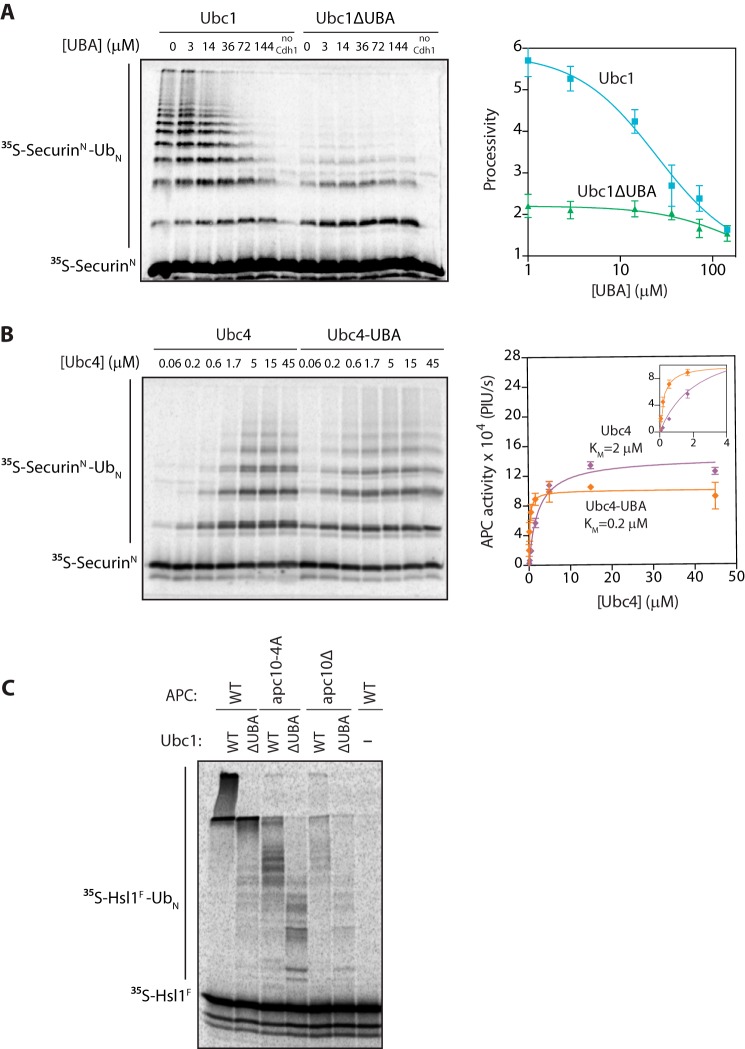
FIGURE 4.
The UBA domain promotes APC/C binding. A, [35S]SecurinN was translated in vitro in rabbit reticulocyte lysate, purified, and mixed with purified APC/C, Cdh1, and varying concentrations of recombinant UBA domain. Ubc1 (either wild type or ΔUBA; 10 μm) charged with wild-type ubiquitin (Ub) was added, and reactions were carried out at room temperature for 15 min. Reaction products were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography with a phosphorimaging system. Autoradiographs were quantified using ImageQuant. The right panel displays quantification of processivity of APC/CUbc1 and APC/CUbc1ΔUBA as a function of the concentration of free UBA domain. Processivity was calculated by quantifying individual ubiquitinated products, multiplying the amount of product by the number of ubiquitins in the product, and dividing by the total amount of modified products. Data were fit to the log(inhibitor) versus response equation in Prism software. The average of three experiments is shown. Error bars represent S.E. B, purified [35S]SecurinN, APC/C, and Cdh1 were combined as in A. Ubc4 or Ubc4-UBA charged with wild-type ubiquitin was added at the indicated concentrations, and reactions were carried out at room temperature for 15 min. Reaction products were analyzed as in A. The right panel displays quantification of the dependence of APC/C activity on concentration of Ubc4 or Ubc4-UBA. Data were fit to the Michaelis-Menten equation in Prism software. The average of three experiments is shown. Error bars represent S.E. The inset shows a close-up of the graph at lower E2 concentrations. PIU/s, phosphorimaging units/s. C, [35S]Hsl1F was translated in vitro in rabbit reticulocyte lysate, purified, and mixed with Cdh1 and APC/C immunoprecipitated from wild-type, apc10Δ mutant, or apc10-4A mutant yeast. E2s (all at 5 μm final concentration) were charged with wild-type ubiquitin and added, and reactions were carried out at room temperature for 15 min. Reaction products were analyzed as in A.