FIGURE 6.
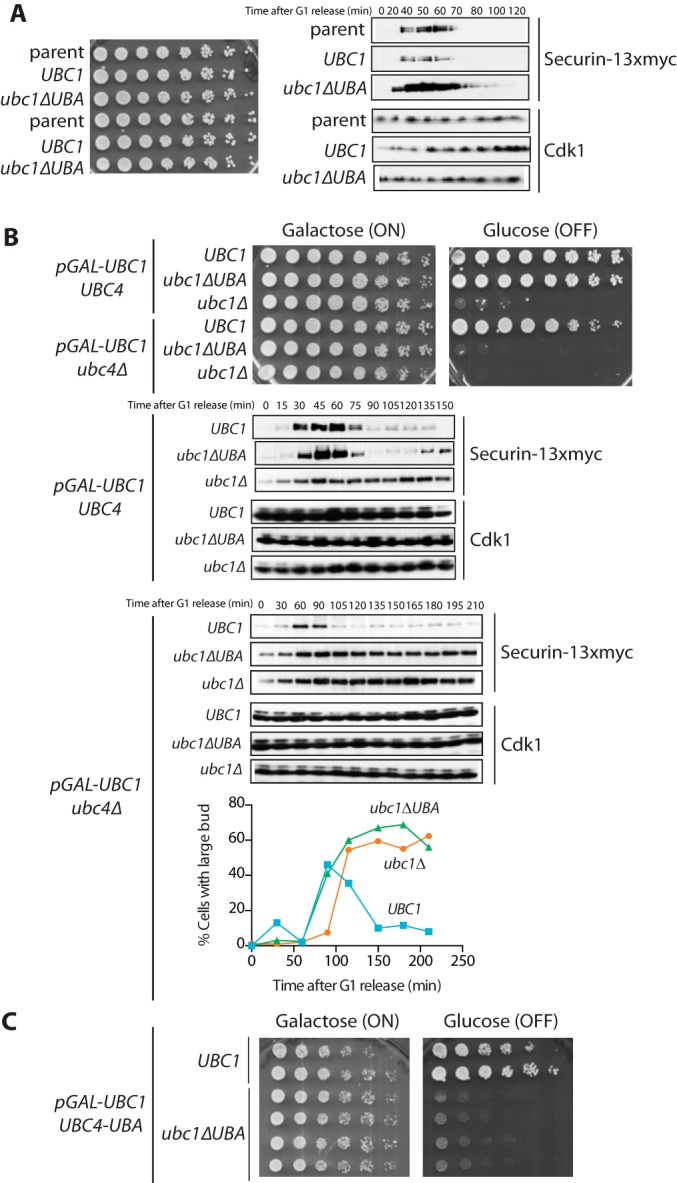
The UBA domain is important for Ubc1 function in vivo. A, left, strains were grown to midlog phase at 30 °C in medium containing 2% glucose, diluted to an A600 of 0.1, plated as serial dilutions on 2% glucose, and grown for 2 days at 30 °C. Right, asynchronous cultures (A600 = 0.2) were arrested in G1 with α factor (1 μg/ml) for 3 h and released from G1 arrest by washing away α factor (zero time point). Cell samples were taken at the indicated times, lysed, and analyzed by Western blotting against the indicated proteins. Results are representative of three independent experiments. B, top, strains were grown to midlog phase at 30 °C in medium containing 2% galactose and raffinose, diluted to an A600 of 0.1, plated as serial dilutions on 2% galactose and raffinose or 2% glucose, and grown for 2 days at 30 °C. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Bottom, asynchronous cultures were arrested in G1 with α factor (1 μg/ml) for 5 h. During the last 2 h of α factor treatment, cultures were incubated with 2% glucose. Cells were released from G1 by washing away α factor, and resuspended in medium containing 2% glucose (zero time point). Cell samples were taken at the indicated times, lysed, and analyzed by Western blotting against the indicated proteins. Parallel samples were taken, and a budding index was counted by microscopy. Results are representative of three independent experiments. C, the indicated strains were grown and plated as in B.
