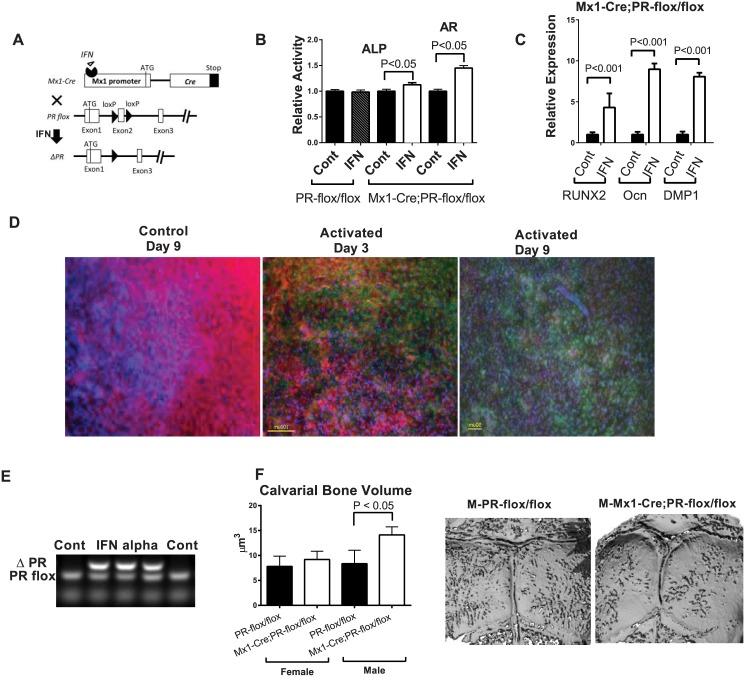
Fig 3. PR inactivation in the Mx1+ calvarial cells and calvariae in vitro.
(A) A schematic diagram showing that PR-flox is crossed to Mx1-Cre. Mx1-Cre can be activated by IFNα to delete exon 2 of the PR gene to generate PR mutants (ΔPR). (B) Mx1-Cre;PR-flox/flox calvarial cells were treated with IFNα (500 units/mL) or without IFNα (control) for three days. The cells were then differentiated into osteoblasts in osteogenic medium without IFNα for 14 days. The relative expressions of RUNX2, Osteocalcin (Ocn) and DMP1 were evaluated by real-time PCR at day 14 and normalized to endogenous β-actin. (C) The cells were collected for alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity assays on day 10 and alizarin red staining (AR) on day 21. The optical density (OD) values were normalized to the corresponding total protein concentrations. Calvarial cells from the PR-flox/flox (without Cre) mice were used as a negative control to exclude the effect of INFα itself. (D) The calvariae obtained from Mx1-Cre;mT/mG double transgenic pups exhibited significant numbers (~40%) of cells that became GFP-positive after three days of IFNα (500 units/mL) treatment, and significantly more cells (~80%) became GFP-positive after an additional six days of culture without IFNα. (E) Genomic DNA was isolated from PR-flox/flox calvarial cells three days after IFNα treatment, and subjected to PR allele-specific PCR. The deleted PR band (ΔPR) indicated Cre-mediated DNA recombination. (F) Five-weeks-old PR-flox/flox or Mx1-Cre;PR-flox/flox mice were injected with pI-pC. Calvariae were collected five months later for microCT analysis for bone volume and (G) representative calvarial images from microCT scans.