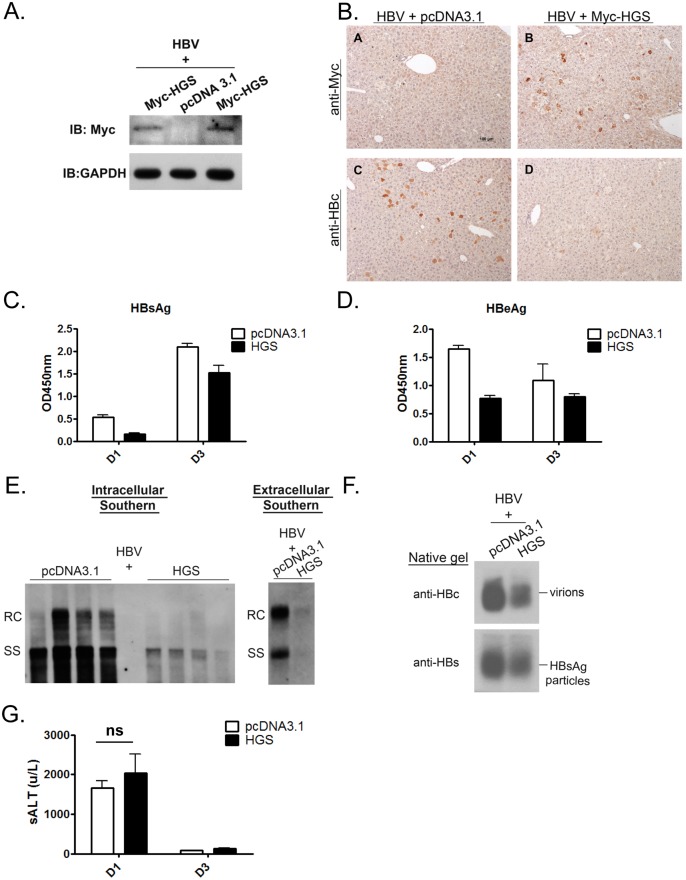
Fig 4. Overexpressed HGS significantly suppressed HBV replication in vivo.
(A) The expression of HGS protein can be detected in the liver sample of hydrodynamically injected mice at 1 dpi by Western blot analysis. Six to eight week old BALB/c mice were tail-vein injected with 14 μg plasmid DNA of an HBV replicon (adr, dimer) and 6 μg DNA of an HGS expression vector or a control plasmid. (B) Immunohistochemistry analysis detected less HBc protein in sectioned liver in the presence of Myc-HGS at 1 dpi. (C) Secreted HBsAg (1000X dilution) and (D) HBeAg (10X dilution) in mouse sera were reduced upon HGS co-injection at 1 and 3 dpi by ELISA. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (E) (left panel) HGS reduced HBV replication in the hydrodynamically injected liver by Southern blot analysis. Each lane represents a liver sample from each mouse. (right panel) HGS reduced HBV DNA in the mouse sera by Southern blot analysis. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (F) HGS reduced the formation of HBV virions and HBsAg particles from pooled mouse sera by 1% native agarose gel electrophoresis at 3 dpi. (G) Liver injurieswere similar between the control and HGS-expressing mice at 1 dpi (p = 0.19 by the Student’s t-test), as measured by the serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels.