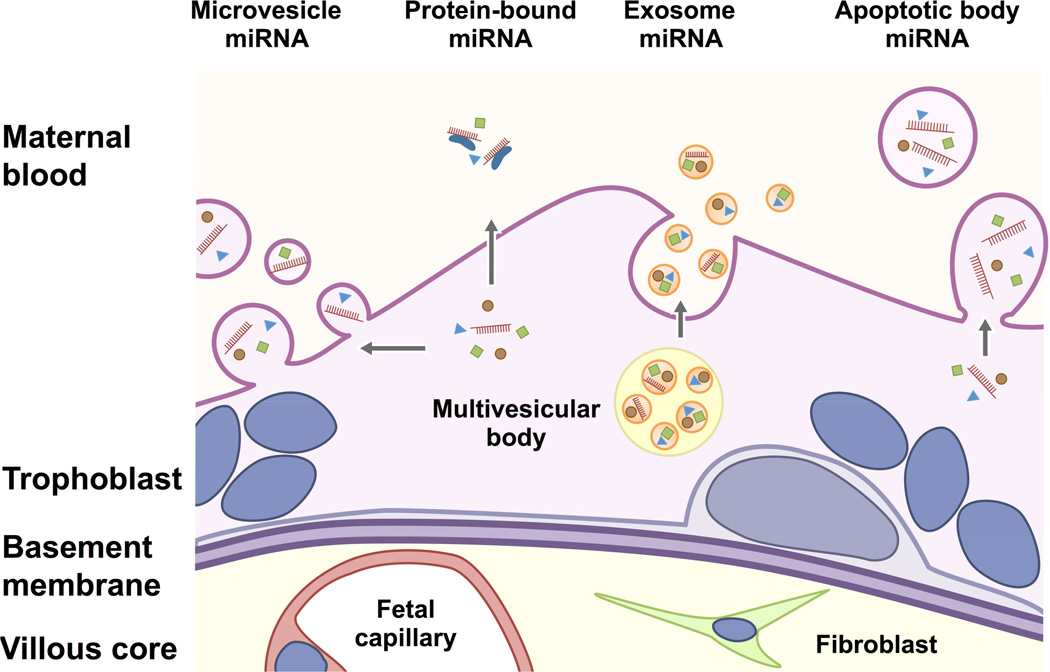
Figure 3. A schematic of extracellular miRNAs derived from human trophoblasts.
MiRNAs can be released from the trophoblast layer in different forms: microvesicle-enveloped form; apoptotic body–enveloped form; nano-sized, exosome-encapsulated form; and RNA-binding, protein-bound form. Exosomes are formed by budding in intraluminal vesicles to form multivesicular bodies (MVB). Some MVBs will fuse with the plasma membrane and release their intraluminal vesicles or exosomes into the extracellular space. In contrast, microvesicles are produced directly by budding and the detachment of membrane vesicles from the plasma membrane. Apoptotic bodies (blebs) derive from cells undergoing apoptotic fragmentation and the formation of membrane-enclosed vesicles also called apoptosomes. The figure was modified from Ouyang.156