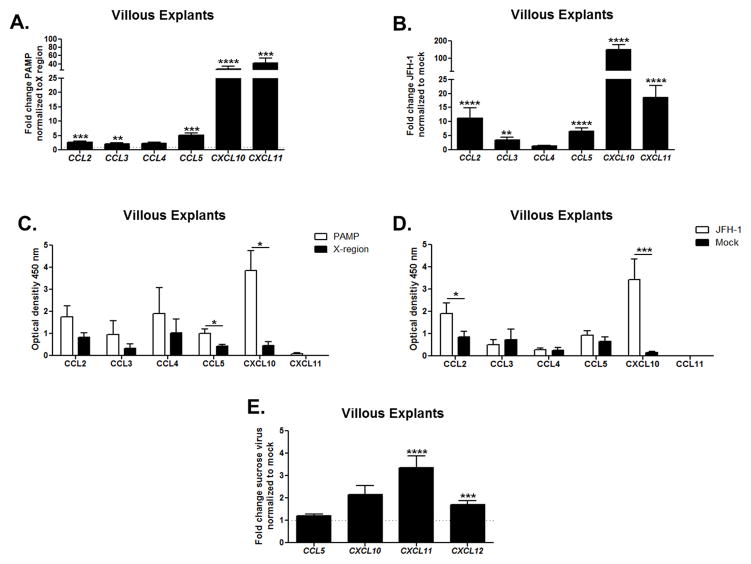
Figure 5. HCV sensing by human trophoblasts induces up-regulation of chemokines at the gene and protein level.
Villous explants were transfected for 24 hours with (A) HCV-PAMP (or the X-region control) and (B) JFH-1 RNA (normalized to mock). Gene up-regulation was assessed by real-time RT-PCR. Bars represent mean plus SEM, Wilcoxon signed-rank test (n=8). Supernatant analysis of (C) villous explants PAMP (or X-region-transfected, n=4) and (D) JFH-1 (or mock transfected, n=8) for 48 hours with Multi-Analyte ELISArray Kit (QIAGEN) confirmed that HCV-PAMP induced statistically higher protein secretion of CCL5 (RANTES) and CXCL10 (IP-10) and that JFH-1 elicited significant higher secretion of CCL2 (MCP1) and CXCL10 (IP-10). Bars represent mean plus SEM, Mann-Whitney test. (E) Villous explants were cultured for 48 hours with sucrose purified JFH-1 virus. Villous explants were dissected from early terminated pregnancy between 10 and 20 week gestation. Gene up-regulation was assessed by real-time RT-PCR. Bars represent mean plus SEM, Wilcoxon signed-rank test (n=8), *<p0.05, ** p<0.01, ***p< 0.001, ****p<0.0001.