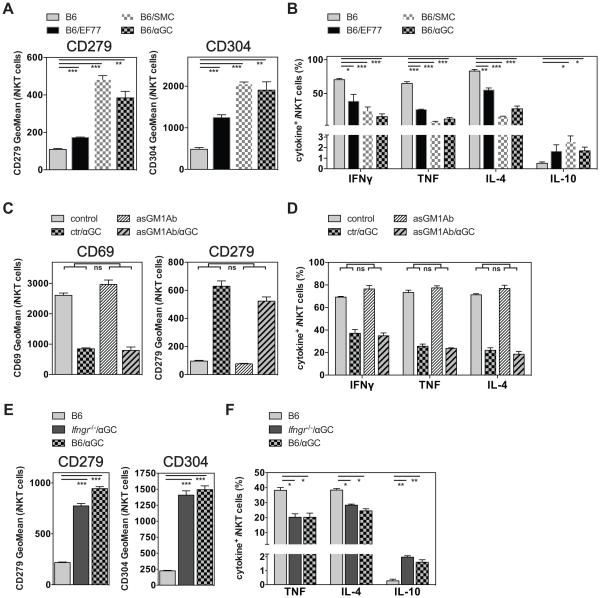
Figure 4. iNKT cell hypo-responsiveness is induced by Th1 - biasing compounds.
(A, B) C57BL/6 (B6) mice were either left untreated or injected i.v. with 4μg of EF77, SMC124 (SMC) or αGalCer (αGC) as indicated. One month later mice were injected i.v. with 1μg αGalCer, and 90 min later splenic iNKT cells were analyzed for the expression of surface makers (A) and intracellular cytokines (B). Statistically significant differences of treated groups versus the control group are indicated. (C, D) Control C57BL/6 (B6) mice or mice NK cell depleted one day earlier with α-asGM1 Ab (asGMAb) were either left untreated or injected i.v. with 4μg αGalCer (αGC). One month later 1μg αGalCer was injected i.v., and splenic iNKT cells were analyzed 90 min later for the expression of surface makers (C) and of intracellular cytokines (D). Statistically significant differences (Anova) of B6(control vs αGC) versus the NK-depleted asGM1(control vs αGC) groups are indicated. ns = not significant. (E, F) Control C57BL/6 (B6) mice or mice deficient for the IFNγ-receptor (Ifngr−/−) were either left untreated or injected i.v. with 4μg αGalCer (αGC). One month later 1μg αGalCer was injected i.v., and splenic iNKT cells were analyzed 90 min later for the expression of surface makers (E) and of intracellular cytokines (F). Statistically significant differences of treated groups versus the control group are indicated. Representative data from one of two independent experiments are shown.