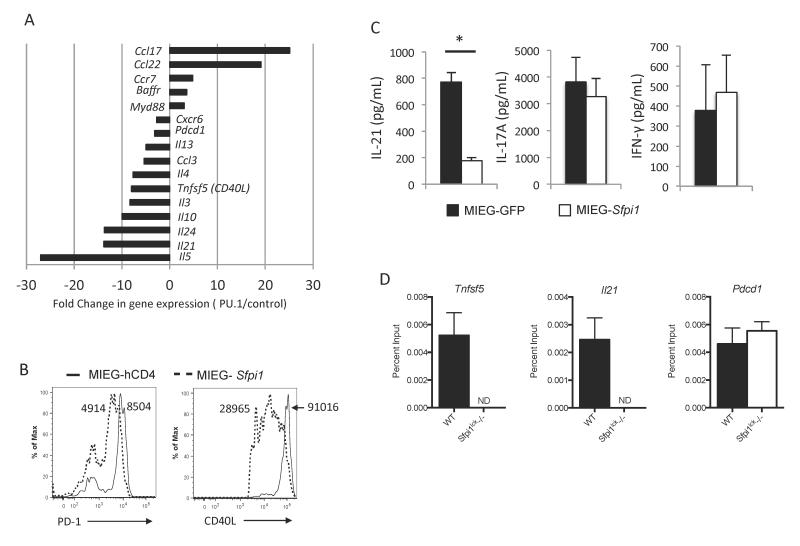
Figure 1.
PU.1-dependent gene regulation in CD4+ T-cells. A, Naïve wild type CD4 T cells were cultured under Th2 conditions and transduced with control retrovirus or retrovirus expressing PU.1. Changes in expression of genes displayed as the ratio of expression of genes in CD4+ T-cells ectopically expressing PU.1 relative to expression in control vector transduced cells. B, Naïve wild type CD4 T cells were cultured under Tfh-like conditions and transduced with control retrovirus or retrovirus expressing PU.1. After five days of culture, transduced cells were stimulated with PMA and Ionomycin for 5 hours and stained for PD-1 and CD40L. Histograms indicate PD-1 and CD40L expression. Numbers indicate MFI. C, Naïve cells from Sfpi1lck−/− mice were cultured under Th17conditions and retrovirally transduced with an empty control vector (MIEG-GFP), or a vector expressing the PU.1 gene, MIEG-Sfpi1. After 5 days of culture, cells were sorted by GFP expression and restimulated with anti-CD3. Supernatants were collected and IL-21, IL-17a, and IFN-γ secretion was measured by ELISA. Data are representative of 3-5 mice/group. D, Chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed from wild type and Sfpi1lck−/− activated T cells cultured for three days. Chromatin was immunoprecipitated with anti-PU.1 and isolated DNA was identified with quantitative PCR for promoter regions of the indicated genes. Statistical significance was determined with a two-tailed t test, *, p<0.05.