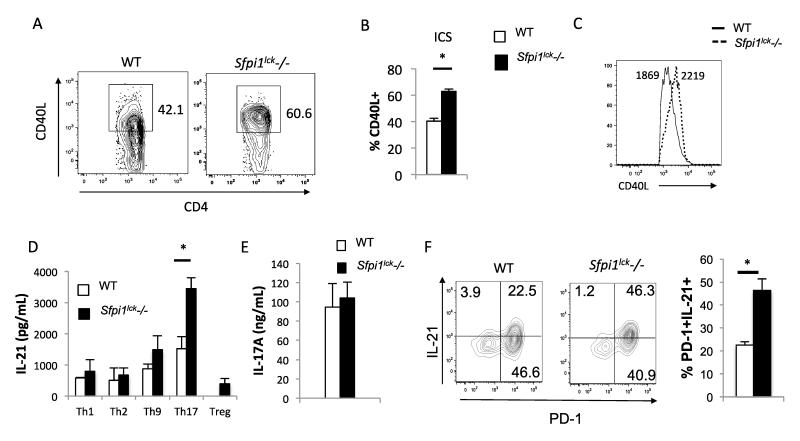
Figure 2.
CD4+ T-cells from Sfpi1lck−/− mice show increased CD40L and IL-21 expression in vitro. Total CD4+ T-cells from Sfpi1lck−/− and WT mice were stimulated with PMA + Ionomycin for 2 hours. A, Flow cytometric analysis of intracellular staining for CD40L. The average percent of CD4+CD40L+ cells (B) and histograms of the MFI of CD40L+ cells (C) are indicated. D, Naïve cells CD4+CD62L+ were isolated from WT and Sfpi1lck−/− mice and cultured under Th1, Th2, Th9, Th17, and T-regulatory conditions. Concentrations of IL-21 (D) produced by the indicated Th subsets, and IL-17A (E) produced by Th17 cells was measured by ELISA. F, Naïve cells from wild type and Sfpi1lck−/− mice were cultured under Tfh conditions. After 3 days of culture cells were restimulated with PMA and Ionomycin for 5 hours and surface and intracellular cytokine staining was conducted. Contour plots indicate PD-1 and IL-21 staining and graphs indicate the average of values from 3 mice. Data are representative of 3-5 mice/experiments. Statistical significance was determined with a two-tailed t test, *, p<0.05.