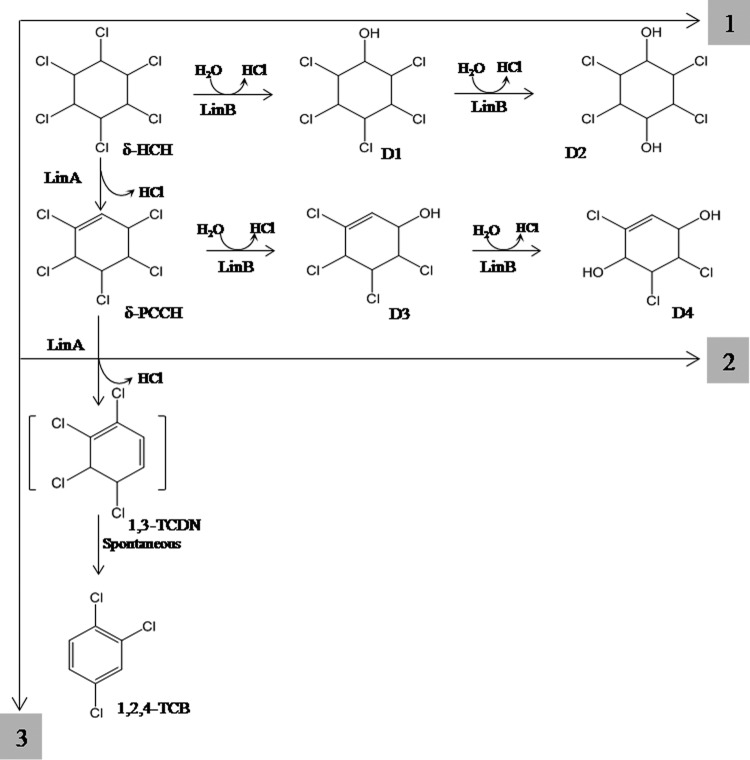
FIG 1.
Three possible pathways for metabolism of δ-HCH, including its conversion by LinB into the metabolites D1 (δ-2,3,4,5,6-pentachlorocyclohexanol) and D2 (δ-2,3,5,6-tetrachlorocyclohexane-1,4-diol) (1); its conversion by LinA into δ-PCCH, followed by conversion by LinB into D3 (δ-3,4,5,6-tetrachloro-2-cyclohexenol) and D4 (δ-3,5,6-trichloro-2-cyclohexene-1,4-diol) (2); and its conversion by LinA into 1,3,4,6-tetrachlorocyclohexa-1,4-diene (1,4-TCDN), followed by spontaneous metabolism to 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene (3).