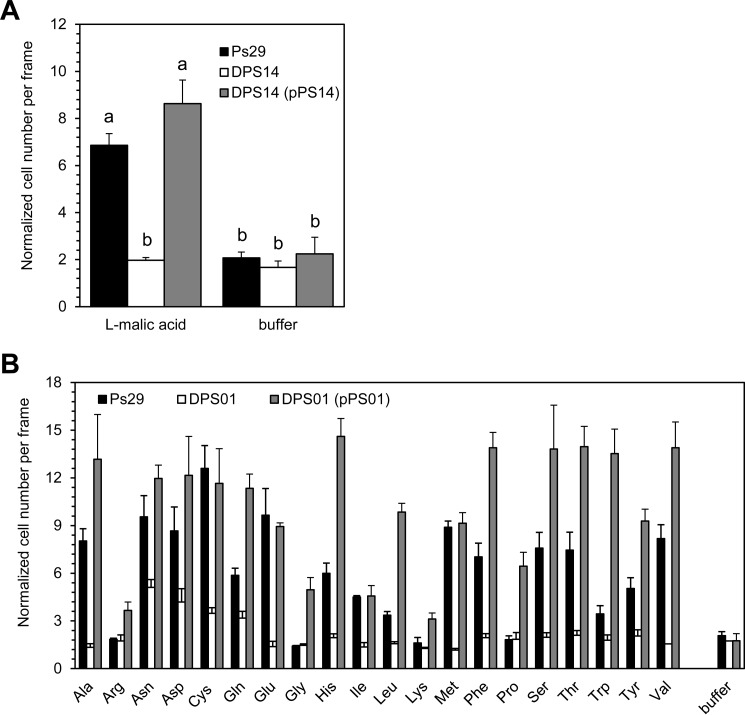
FIG 2.
Chemotactic responses to amino acids and l-malate by mutant and complemented R. pseudosolanacearum Ps29 strains. Bacterial cells were grown for 4 h in RSM medium after preculture in CPG medium with or without kanamycin. Buffer indicates 10 mM HEPES buffer as a negative control. (A) Chemotactic responses to 0.5 mM l-malate by R. pseudosolanacearum wild-type strain Ps29, the mcpM deletion mutant (DPS14), and DPS14 harboring the complementing plasmid [DPS14(pPS14)]. Videotape frames were analyzed at the initiation of observation and 1 min after initiation. Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05 by Student's t test). (B) Chemotactic responses to 5 mM naturally occurring amino acids by R. pseudosolanacearum wild-type strain Ps29, the mcpA deletion mutant (DPS01), and DPS01 harboring the complementing plasmid [DPS01(pPS01)]. Videotape frames were analyzed at the initiation of observation and 1 min after initiation, except for Asp and Cys. Chemotactic responses to Asp and Cys were analyzed 1.5 min after initiation. There are significant differences in chemotaxis toward naturally occurring amino acids other than Arg, Gly, Lys, and Pro between the wild-type strain and DPS01 (P < 0.05 by Student's t test) and between DPS01 and DPS01(pPS01) (P < 0.05 by Student's t test). There were no significant differences in chemotaxis to Arg, Gly, Lys, and Pro between the wild-type strain and DPS01, although chemotactic responses of DPS01 and DPS01(pPS01) were significantly different (P < 0.05 by Student's t test). Vertical bars represent the standard errors for measurements done at least in triplicate.