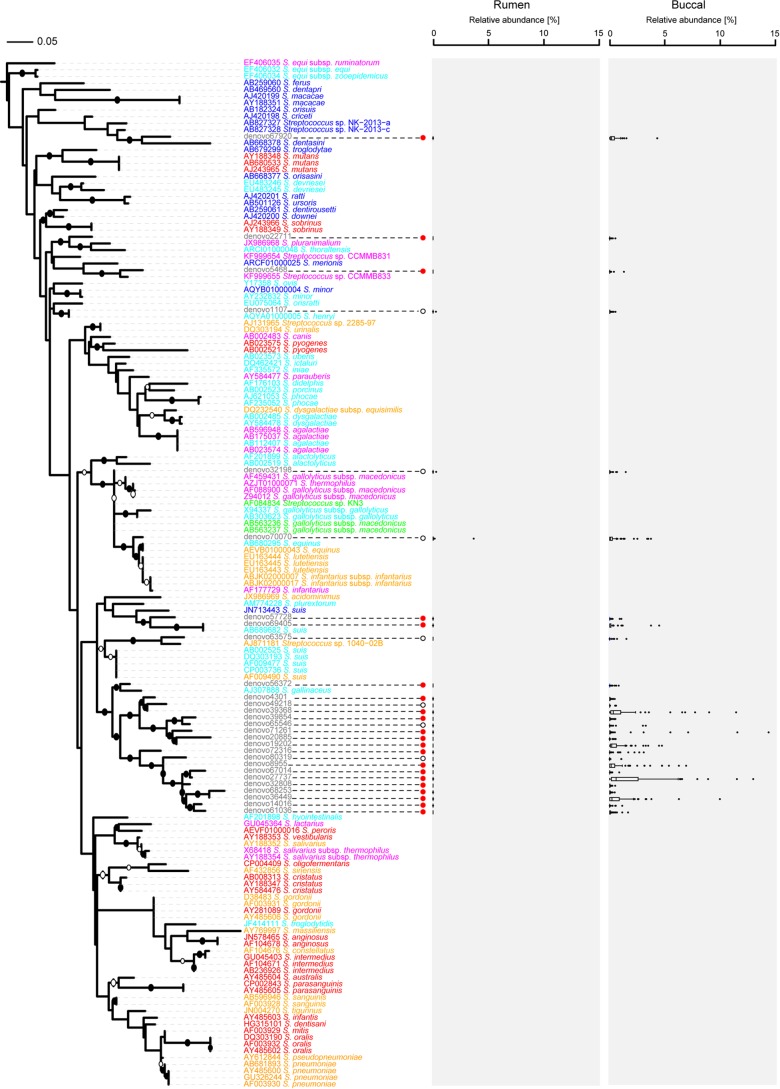
FIG 2.
Phylogenetic tree of 126 Streptococcus reference sequences, constructed using RAxML, with 1,000 bootstrap replications. Representative sequences from 28 OTUs (gray font) assigned to the genus Streptococcus were added using the ARB parsimony insertion tool with the ssuref:bacteria filter and E. coli positions 28 to 288. Bootstraps with values of >70% and >90% were inferred and are marked as open and closed circles, respectively, on the branches. Several sequences belonging to the genus Fusobacterium were used as an outgroup. Species names are colored according to the habitats from which the species were isolated: red, human oral species; orange, human-associated species; blue, animal oral species; light blue, animal-associated species; magenta, dairy product species; and green, rumen species. Filled red circles indicate significant differences in relative abundances between samples collected using the two different methods, while open circles indicate no significant difference. Box plots show the median relative abundances and lower (25%) and upper (75%) percentiles for samples collected via stomach tubing (rumen) or buccal swabs (buccal). Outliers are shown as individual dots. The scale bar indicates 0.05 nucleotide substitution per nucleotide position.