Fig. 2.
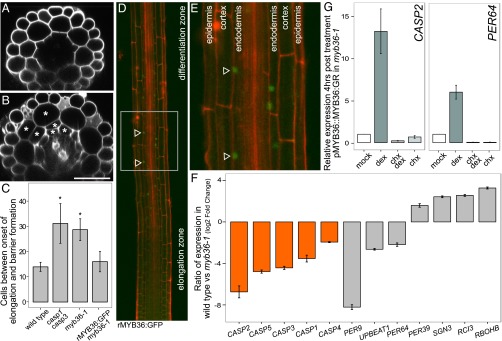
myb36-1 mutant seedlings exhibit delayed barrier formation and dramatic changes in gene expression. (A) Optical cross-section of wild-type root in the differentiation zone. (B) Optical cross-section of myb36-1 mutant root displays Casparian strip defect and extra cell divisions (asterisks). (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (C) Quantification of cells after onset of differentiation in wild type, casp1 casp3, and myb36-1 and genetic complementation of myb36-1 with rMYB36:GFP seedlings. Error bars are SD of the mean from three biological replicates. Significance was determined by Student’s t test, *P < 0.01 (for source data see Dataset S5). (D) Confocal images (25×) stitched together to reveal rMYB36:GFP expression. The fusion is most strongly detected in the elongation zone, before the onset of differentiation (arrowheads). (E) rMYB36:GFP is expressed specifically in the nuclei in the endodermis (arrowheads). Epidermis, cortex, and endodermis are labeled for orientation. (F) myb36-1 mutant endodermis has reduced expression of CASP genes (orange) and altered expression of many genes involved in oxidoreductase activity (gray) compared with wild-type endodermis. Error bars are SEM from three biological replicates. Adjusted P value ≤ 0.01 (Methods) (for source data see Dataset S6). (G) qRT-PCR of two putative MYB36 targets 4 h after induction of pMYB36::MYB36:GR. Mean expression values of three biological replicates are reported after normalization with PP2A expression. Error bars are SEM (for source data see Dataset S7).
