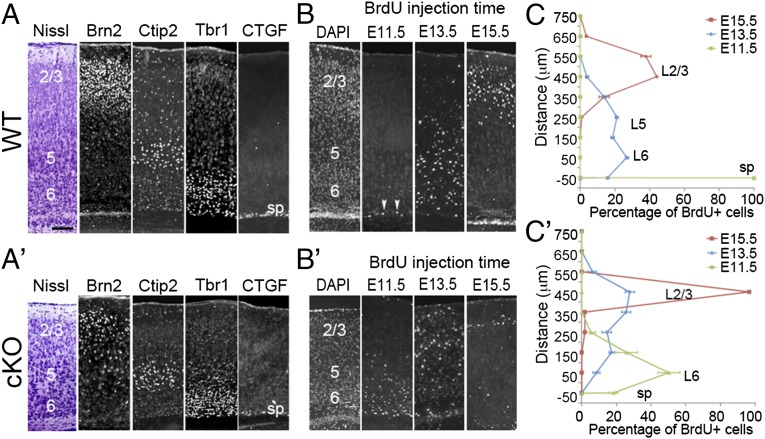
Fig. 1.
Lhx2 regulates the timing of sequential neurogenesis. (A and A′) Immunostaining for markers of specific cortical layers on coronal sections of P7 WT (A) and cKO (A′) cortices. In both WT and cKO samples, six neuronal layers are present, including the Brn2-expressing L2/3 (2/3), Ctip2-expressing L5 (5), Tbr1-expressing L6 (6), and CTGF-expressing subplate (sp). (B and B′) Immunostaining for BrdU on coronal sections of P7 WT (B) and cKO (B′) cortices. BrdU was injected into pregnant mothers at E11.5, E13.5, or E15.5. BrdU injected at E11.5 labeled neurons distributed in the subplate in WT mice (arrowheads), but BrdU-labeled cells were detected in layer 6 in cKO mice. BrdU injected at E13.5 labeled neurons concentrated in layer 6 in WT mice, but E13.5 BrdU-labeled cells were spread to L2/3 in cKO mice. BrdU injected at E15.5 labeled many neurons in L2/3 in WT, but only a few superficially in L2/3 in cKO. (C and C′) Quantification of results from B and B′ indicating the location of BrdU-positive neurons in P7 WT and cKO cortices labeled at indicated times (n = 3). In a 100-μm-wide radial column, BrdU-labeled neurons were counted at 100-μm intervals from the subplate (defined as 0) to the pial surface. The percentage of BrdU-positive cells was calculated by determining the number of BrdU-positive cells in a 100 × 100 μm box divided by the total number of BrdU-positive cells in the entire radial column. (Scale bar, 100 μm.)