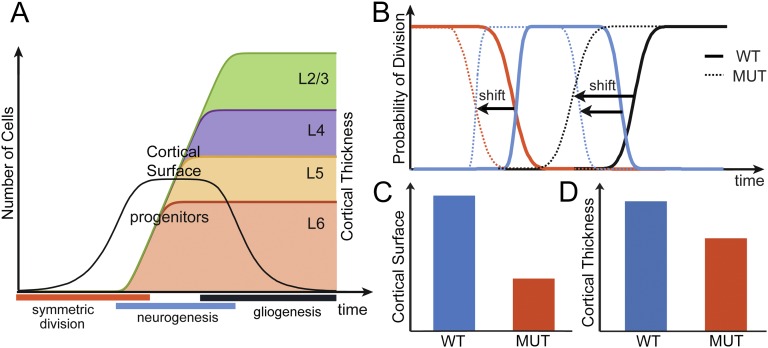
Fig. 5.
Theoretically deciphering the effect of Lhx2 deletion. (A) Evolution of the number of progenitors (black line) and number of neurons in each layer as a function of time. Symmetric division (red) duplicates the number of progenitors, neurogenesis (blue) gives rise to neurons, and gliogenesis (black) decreases the pool of progenitors. (B) Comparison between fitted models to WT and cKO (MUT, dotted lines). In cKO, the precocious end of symmetric division and neurogenesis leads to decreased cortical surface (C) and thickness (D).