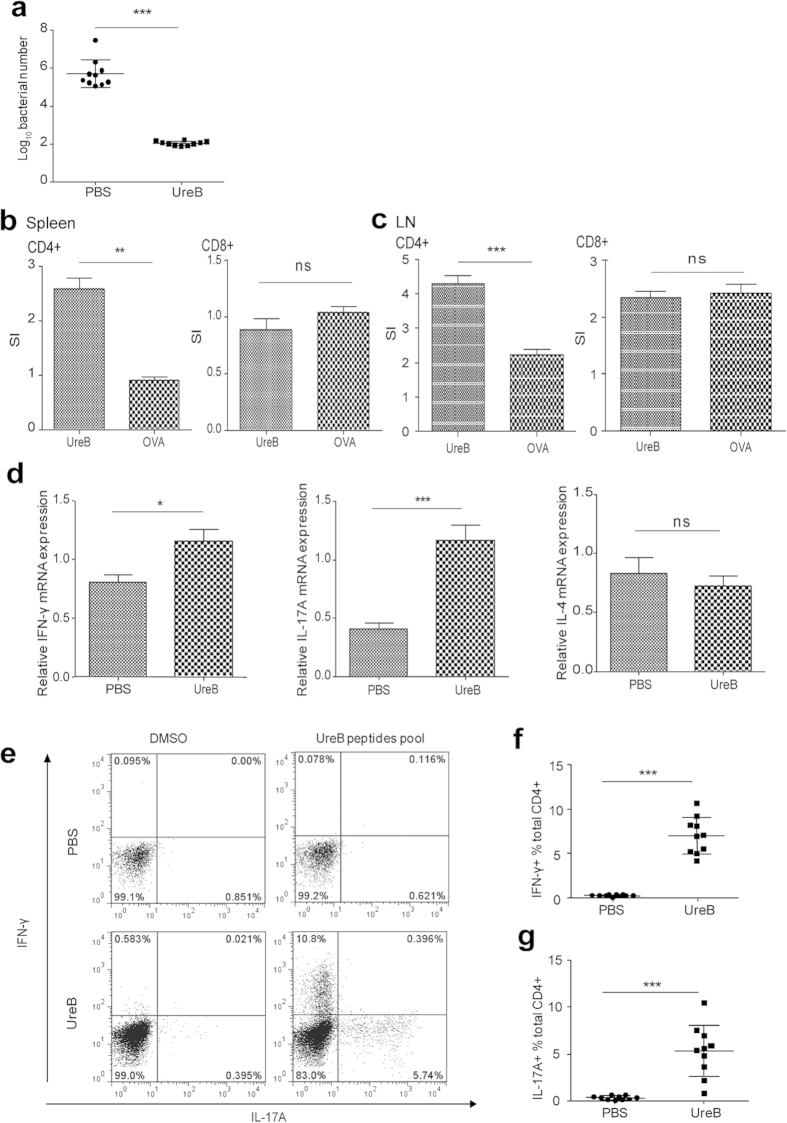
Figure 1. Types of CD4+ T-cell responses elicited via UreB immunization.
(a) H. pylori colonization of the gastric mucosa of UreB-immunized mice at 4 weeks after the last infection. (b) Proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells isolated from the spleens of UreB-immunized mice was assessed using the 3H-TdR incorporation assay. (c) The proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells isolated from stomach-draining lymph nodes of UreB-immunized mice was assessed using the 3H-TdR incorporation assay. (d) IFN-γ, IL-17A and IL-4 mRNA levels in CD4+ T cells isolated from UreB-immunized mice were analyzed. (e) Splenic lymphocytes from UreB-immunized mice or PBS controls were cultured in vitro in the presence of recombinant UreB. IFN-γ-producing and IL-17A-producing CD4+ T cells were assessed using the UreB peptide pool on day 7. (f) IFN-γ-producing CD4+ T-cell responses of all immunized mice were assayed. (g) IL-17A-producing CD4+ T-cell responses of all immunized mice were assayed. All results were repeated more than three times. The data are expressed as the mean ± S.D (n = 10). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.