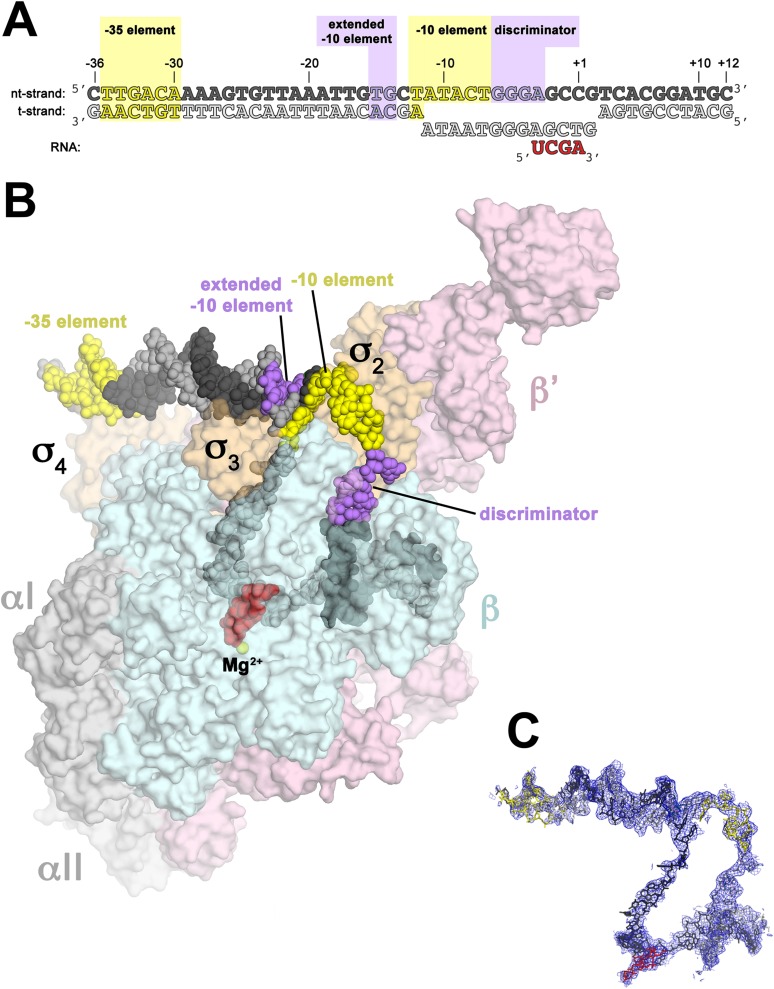
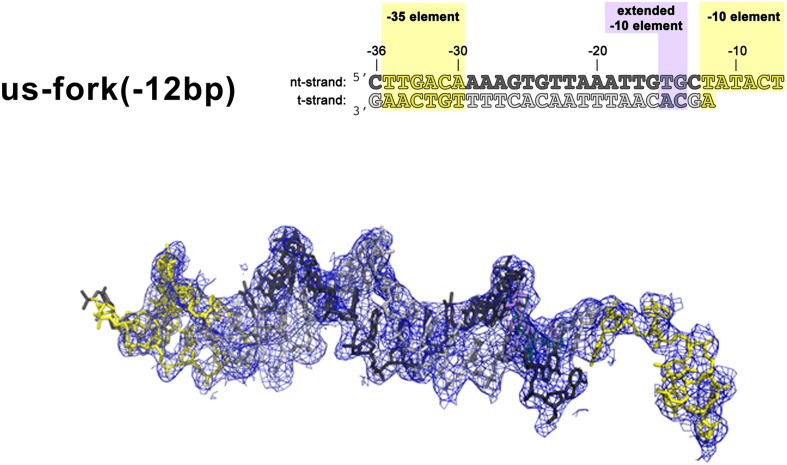
Figure 1. Structure of RPo.
(A) Oligonucleotides used for RPo crystallization. The numbers above denote the DNA position with respect to the transcription start site (+1). The DNA sequence is derived from the full con promoter (Gaal et al., 2001). The −35 and −10 (Pribnow box) elements are shaded yellow, the extended −10 (Keilty and Rosenberg, 1987) and discriminator (Feklistov et al., 2006; Haugen et al., 2006) elements purple. The nt-strand DNA (top strand) is colored dark grey; t-strand DNA (bottom strand), light grey; RNA transcript, red. (B) Overall structure of RPo. The nucleic acids are shown as CPK spheres and color-coded as above. The Taq EΔ1.1σA is shown as a molecular surface (αI, αII, ω, grey; β, light cyan; β′, light pink; Δ1.1σA, light orange), transparent to reveal the RNAP active site Mg2+ (yellow sphere) and the nucleic acids held inside the RNAP active site channel. (C) Electron density and model for RPo nucleic acids. Blue mesh, 2Fo − Fc maps for nucleic acids (contoured at 0.7σ).