Figure 2.
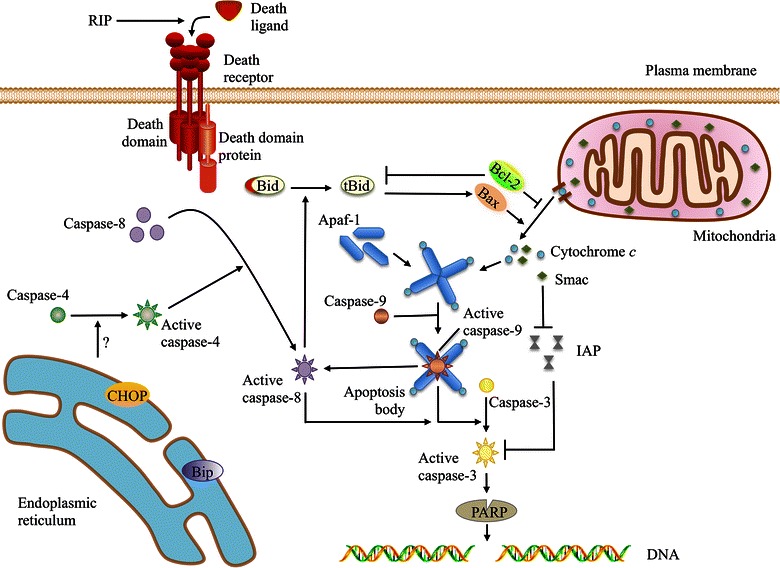
The apoptotic mechanism of RIPs. RIPs may trigger the death receptor pathway by facilitating the combination of the death ligand and its receptor. Caspase-8 is recruited and activated by death domain proteins such as Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD). C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) and immunoglobulin-binding protein (Bip) are increased under RIP-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress, in which activated caspase-4 contributes to capase-8 activation. The release of second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases (Smac) and cytochrome c, which can be increased by Bax or decreased by Bcl-2, is promoted by RIP. Cytochrome c aggregates with apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 (Apaf-1) and becomes an apoptotic body that activates caspase-9, which in turn activates caspase-3 and caspase-8. Activated caspase-3 cleaves poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), resulting in DNA fragmentation and apoptosis. Smac protects caspase-3 from inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) inhibition. Caspase-8 cuts Bid into tBid, which is necessary for Bax oligomerization in the mitochondrial outer membrane. The inhibition of tBid insertion into the mitochondrial membrane by Bcl-2 prevents cytochrome c release [31].
