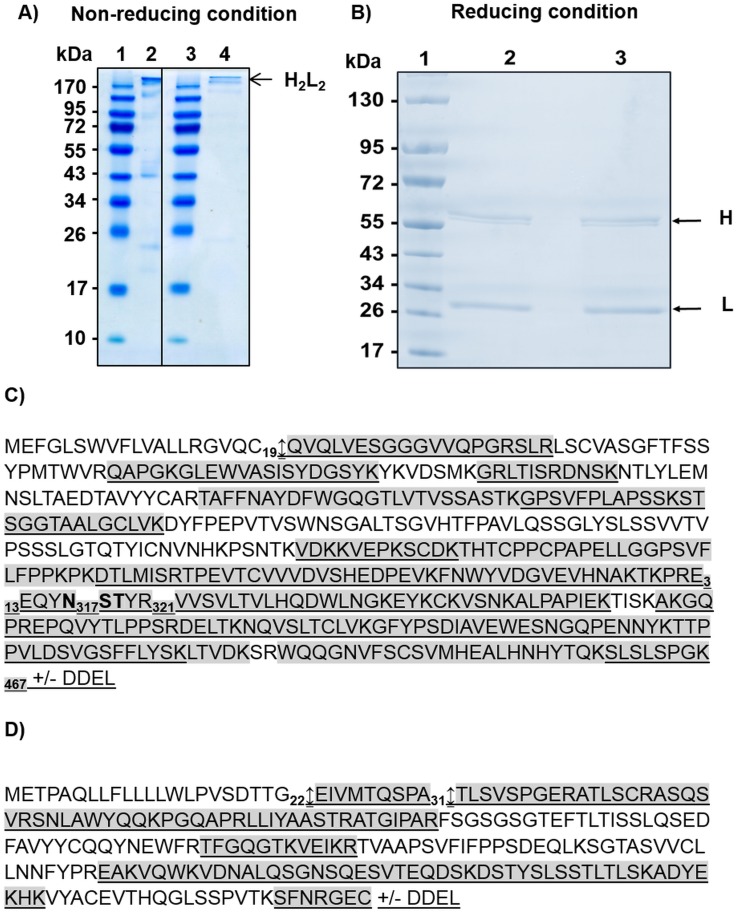
Fig 1. Protein analysis of algae-made HBsAg recombinant antibodies.
A) SDS-PAGE gel in non-reducing conditions and stained with Coomassie blue. Lane 1: Molecular Weight; Lane 2: secreted mAb (1 μg); Lane 3: Molecular Weight; Lane 4: ER-retained mAb (1 μg). B) NuPAGE gel electrophoresis of mAbs produced in P. tricornutum. The gel has been run under reducing conditions and was stained with Coomassie blue. Lane 1: Molecular Weight; Lane 2: secreted mAb (3 μg); Lane 3: ER-retained mAb (3 μg). C) Heavy chain protein sequence of the antibody directed against HBsAg produced in P. tricornutum (GenBank accession number JF970210) plus or minus the DDEL ER-retention signal. This sequence include the signal peptide and the methionine is the first amino acid. D) Light chain protein sequence of the antibody directed against HBsAg produced in P. tricornutum (GenBank accession number JF970211) plus or minus the DDEL ER-retention signal. This sequence include the signal peptide and the methionine is the first amino acid. The peptides highlighted in grey are the ones which have been observed by LC-ESI MS analysis of tryptic digests for the heavy chain of the secreted mAb and for light chains of both ER-retained and secreted mAbs. The underlined peptides are the ones which have been observed by LC-ESI MS analysis of tryptic digests for the heavy chain of the ER-retained mAb. The heavy chain potential N-glycosylation site is in bold (N317ST). The arrows indicate the signal peptide cleavage sites.