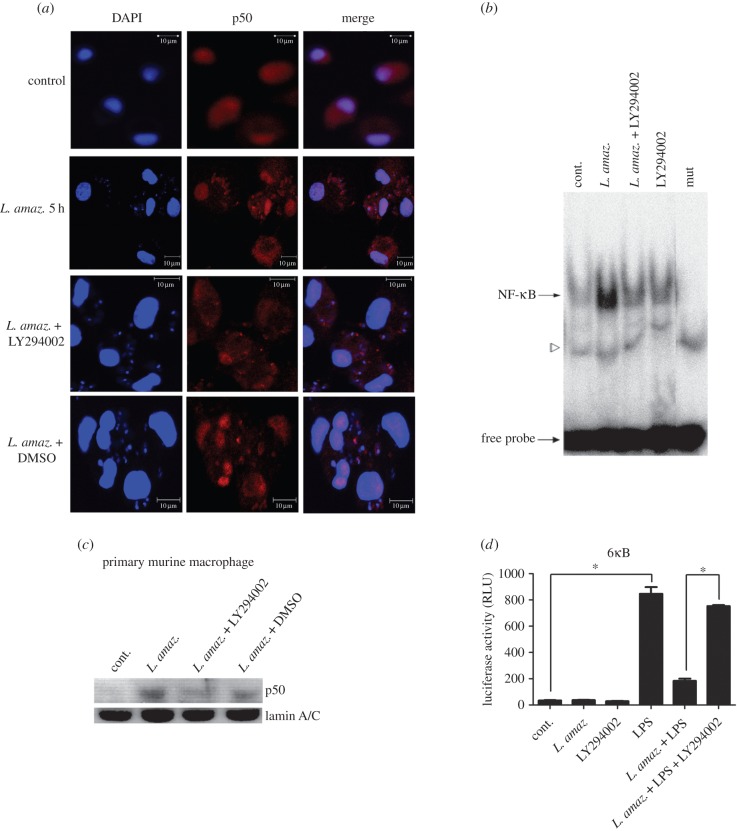
Figure 3.
The PI3K/Akt pathway is involved in NF-κB activation during L. amazonensis infection. (a) Confocal photomicrographs from the infection conditions indicated immunostained with p50 (red) and nuclei stained with DAPI (blue), using 100× objective (bar = 10 µm). Primary human macrophages infected with L. amazonensis for 5 h display higher expression of p50 in nuclei. (b) Macrophages were infected with promastigotes of L. amazonensis and treated with LY 294002 for 1 h. Nuclear extracts were obtained and subjected to EMSA as indicated; mut, NF-κB mutant oligonucleotide. The specific bands of NF-κB are indicated by arrows and a free probe is indicated by the bottom arrow. (c) Nuclear protein lysates were obtained from primary murine macrophages and submitted to western blot using anti-p50 specific antibody or anti-lamin A/C. (d) RAW 264.7 cells were transiently transfected with the reporter plasmid containing the luciferase gene under the control of six NF-κB consensus binding sites. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were infected and/or treated as indicated. After 24 h, the total protein lysate was analysed for Renilla normalized luciferase activity. RLU, luciferase relative unit. *p < 0.05.