Figure 2. Sirt6-dependent regulation of core pluripotent genes.
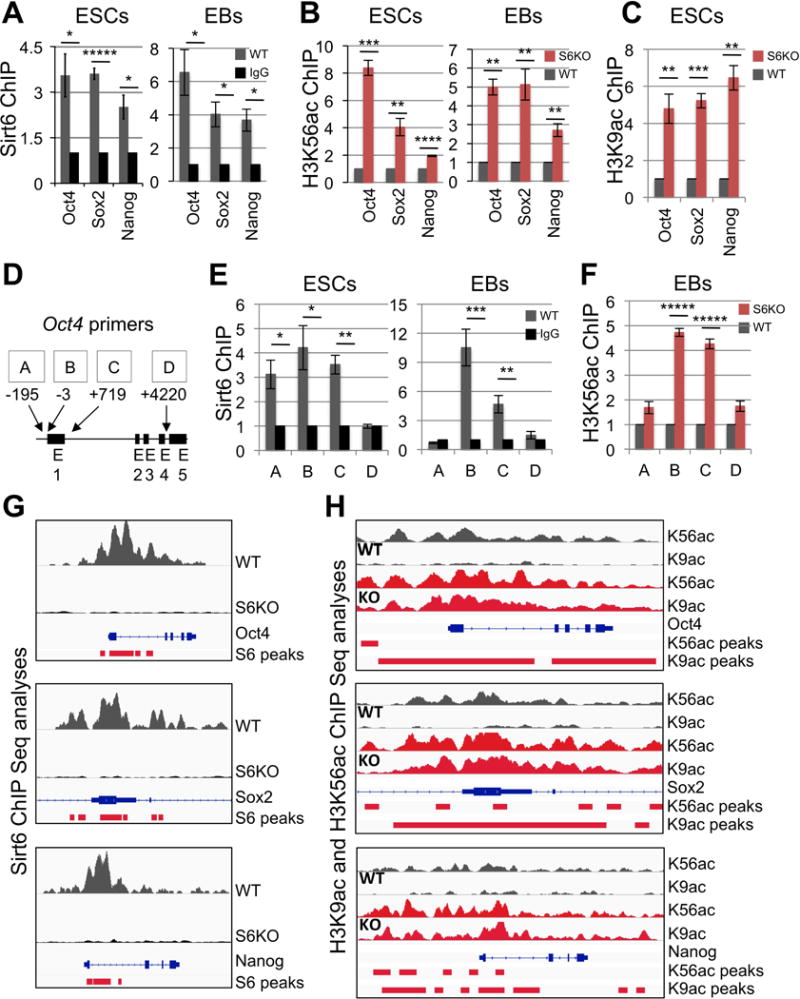
(A) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis for Sirt6 on core pluripotent gene promoters in WT ESCs and EBs. Data is expressed relative to IgG-ChIP control.
(B) ChIP analysis for H3K56ac on core pluripotent gene promoters in both ESCs and EBs from WT and S6KO. Data is expressed relative to WT values.
(C) ChIP analysis for H3K9ac on core pluripotent gene promoters in EBs from WT and S6KO. Data is expressed relative to WT values.
(D) Schematic diagram of the Oct4 locus depicting primers used for ChIP assays in panels (E) and (F).
(E) ChIP analysis for Sirt6 on the Oct4 locus in WT ESCs and EBs. Data is expressed relative to IgG-ChIP control.
(F) ChIP analysis for H3K56ac on the Oct4 locus in EBs from WT and S6KO. Data is expressed relative to WT values.
(G) Sirt6 ChIP-Seq binding profiles on Oct4, Sox2, and Nanog genes in WT and S6KO ESCs. Images were created with the Integrative Genomic Viewer (IGV) (Robinson et al., 2011). Data are normalized to total counts, and the scale rage is 0.0 – 7.0.
(H) ChIP-Seq binding profiles of histone marks H3K56ac and H3K9ac on Oct4, Sox2 and Nanog genes in WT and S6KO ESCs. Images were created with the Integrative Genomic Viewer (IGV) (Robinson et al., 2011). Data are normalized to total counts, and the scale rage is 0.0 – 2.0.
The red bars under each plot in panels (G) and (H) represent statistically significant peaks for each ChIP seq analysis.
